最多包含 M 個連續節點值為 K 的根到葉路徑的數量
介紹
二叉樹是一種引人入勝的資料結構,在計算機科學和程式設計中有著廣泛的應用。一個有趣的問題是從給定的樹中找到從根節點到葉子節點的路徑數量,該樹由父節點及其子節點組成。二叉樹由節點組成,根節點是確定的,並且根據使用者的需要可以指定子節點。K 值是確定的,並且 M 值決定了遍歷的方式。
根到葉路徑的數量
圖是用各種節點建立的,這些節點以整數的形式儲存值。本文主要關注從起始點或根節點到葉子節點或子節點的路徑數量的查詢。
示例
圖是從二叉樹建立的,包含各種節點。
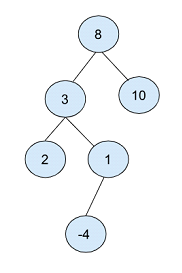
在上面的二叉樹中,根節點選擇為“8”。
然後建立兩個節點,一個值為 3,另一個值為 10,分別佔據根節點的左子節點和右子節點位置。
以值為 2 的節點為根節點,再建立兩個子節點,值為 2 和 1,分別位於左側和右側。
最後,值為 1 的子節點建立了一個值為 -4 的子節點。
方法 1:使用遞迴函式計算最多包含 M 個連續節點值為 K 的根到葉路徑的數量的 C++ 程式碼
為了有效地解決這個問題,我們將利用樹遍歷演算法和遞迴等基本概念。
演算法
步驟 1:建立一個結構來表示樹節點,其中包括兩個指標(左子節點和右子節點)以及一個用於儲存節點值的整數字段。
步驟 2:設計一個遞迴函式,從二叉樹的根節點開始遍歷,同時跟蹤當前路徑長度(初始化為 0)、連續出現次數(最初設定為 0)、目標值 K 和最大允許連續出現次數 M。
步驟 3:根據需要,在每個左子樹和右子樹上遞迴呼叫該函式,傳遞更新的引數,例如遞增的路徑長度和連續出現次數。
步驟 4:在遍歷過程中,對於每個訪問到的非空節點
a) 如果其值等於 K,則將這兩個變數都加 1。
b) 如果其值不匹配 K 或已經超過了路徑中遇到的 M 個連續出現次數,則將變數重置為零。
步驟 5:在遍歷樹的過程中,如果子節點在左子節點和右子節點的情況下值都為零,我們可以用兩種方式處理:
a) 檢查變數是否沒有超過 M。
b) 如果是,則將滿足條件的從起始到結束的路徑總數加 1。
示例
//including the all in one header
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//creating structure with two pointers as up and down
struct Vertex {
int data;
struct Vertex* up;
struct Vertex* down;
};
//countPaths function declared with five arguments ; with root = end; Node= vertex; left = up; right = down
int countPaths(Vertex* end, int K, int M, int currCount, int
consCount) {
//To check the condition when the root is equal to 1 and greater than the maximum value, the values is incremented
if (end == NULL || consCount > M) {
return 0;
}
//To check when the root is equal to the K value, increment by 1
if (end->data == K) {
currCount++;
consCount++;
} else {
//If it is not equal, it will return 0
currCount = 0;
}
if (end->up == NULL && end->down == NULL) {
if (currCount <= M) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
return countPaths(end->up, K, M, currCount, consCount) + countPaths(end->down, K, M, currCount, consCount);
}
//Main function to test the implementation
int main() {
Vertex* end = new Vertex();
end->data = 8;
end->up = new Vertex();
end->up->data = 3;
end->down = new Vertex();
end->down->data = 10;
end->up->up = new Vertex();
end->up->up->data = 2;
end->up->down = new Vertex();
end->up->down->data = 1;
end->up->down->up = new Vertex();
end->up->down->up->data = -4;
int K = 1; // Value of node
int M = 2; // Maximum consecutive nodes
int currCount = -1; // Current count
int consCount = -1; // Consecutive count
cout << "The number of paths obtained from the given graph of" << M << "nodes with a value of " << K << " is " << countPaths(end, K, M, currCount, consCount) << endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
The number of paths obtained from the given graph of 2 nodes with a value of 1 is 3
結論
在本文中,我們探討了計算從頂部(即葉子節點到末端或根節點)開始的路徑數量的問題。透過在 C++ 中使用樹遍歷演算法和遞迴技術,可以有效地解決此類問題。遍歷二叉樹的過程看起來很困難,但透過示例,它變得很簡單。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP