C++程式設計中不使用遞迴列印根到葉路徑。
給定二叉樹,程式必須找出從根到葉的多個路徑,這意味著應該列印所有路徑,但挑戰是不使用遞迴。
我們將迭代遍歷樹,因為約束是不使用遞迴。為了實現這一點,我們可以使用一個STL map,它將儲存根元素,並且每當透過層序遍歷識別葉節點時,它將列印從根到葉的路徑,因為有一個map指標指向根節點。
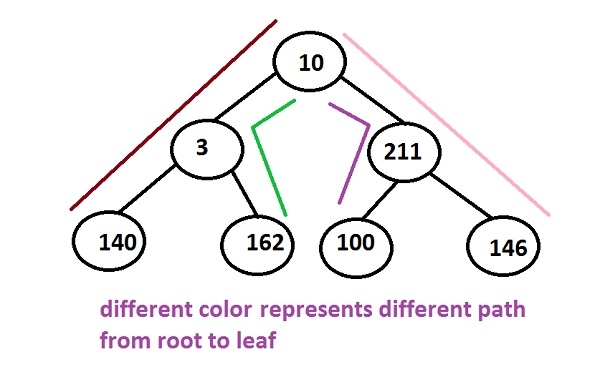
在上圖的樹中,可以生成多條從根到葉的路徑:
10 -> 3 -> 140 10 -> 3 -> 162 10 -> 211 -> 100 10 -> 211 -> 146
因此,程式必須將所有給定的路徑作為給定二叉樹的輸出打印出來。
演算法
START Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct Node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node->data = data node->left = node->right = NULL; return (node) Step 3 -> create function to calculate the path void calculatePath(Node* curr, map<Node*, Node*> first) create STL stack<Node*> stk Loop While (curr) stk.push(curr) curr = first[curr] End Loop While !stk.empty() curr = stk.top() stk.pop() print curr->data End Step 4 -> create function to find the leaf nodes void leaf(Node* root) IF root = NULL Return End Create STL stack<Node*> stc stc.push(root) Create STL map<Node*, Node*> prnt prnt[root] = NULL Loop while !stc.empty() Node* curr = stc.top() stc.pop() IF!(curr->left) && !(curr->right) calculatePath(curr, prnt) End IF curr->right prnt[curr->right] = curr stc.push(curr->right) End IF curr->left prnt[curr->left] = curr stc.push(curr->left) End End STOP
示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//structure of a node
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int data){
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//this function will calculate the path
void calculatePath(Node* curr, map<Node*, Node*> first){
stack<Node*> stk;
while (curr){
stk.push(curr);
curr = first[curr];
}
while (!stk.empty()){
curr = stk.top();
stk.pop();
cout << curr->data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//this function will lead to the leafs
void leaf(Node* root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
stack<Node*> stc;
stc.push(root);
map<Node*, Node*> prnt;
prnt[root] = NULL;
while (!stc.empty()){
Node* curr = stc.top();
stc.pop();
if (!(curr->left) && !(curr->right))
calculatePath(curr, prnt);
if (curr->right){
prnt[curr->right] = curr;
stc.push(curr->right);
}
if (curr->left){
prnt[curr->left] = curr;
stc.push(curr->left);
}
}
}
int main(){
Node* root = newNode(67); //it will insert the nodes to create a tree
root->left = newNode(34);
root->right = newNode(89);
root->left->left = newNode(23);
root->left->right = newNode(95);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
leaf(root); //call the function leaf
return 0;
}輸出
如果我們執行上述程式,它將生成以下輸出
67 34 23 67 34 95 67 89 12

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP