C++中統計位於給定範圍內的BST子樹
給定一個二叉搜尋樹作為輸入。目標是找到BST中節點值介於起始值和結束值之間的子樹數量。如果起始值為5,結束值為50,則統計BST中所有節點權重大於等於5且小於等於50的子樹。
輸入 - 下面的樹 - 範圍 [3-6]

輸出 - 位於範圍內的樹的數量 - 2
解釋 - 只有節點4和6。它們的子樹(NULL)位於3-6之間。
輸入 - 下面的樹:範圍 [12-20]
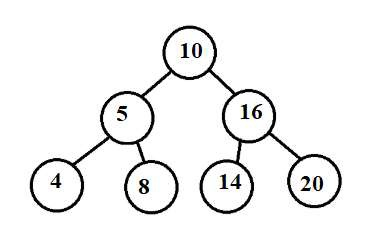
輸出 - 位於範圍內的樹的數量 - 3
解釋 - 對於節點16、14和20。它們的子樹位於12-20之間。
下面程式中使用的方法如下
結構體Btreenode用於建立一個樹的節點,其資訊部分為整數,自引用左指標和右指標指向子樹。
函式Btreenode* insert(int data) 用於建立一個數據為資訊且左右指標為NULL的節點。
透過對給定結構呼叫插入函式來建立BST。將節點新增到根節點的右邊 (root->right = insert(70);) 和根節點的左邊 (root->left = insert(30);)。
變數l和h用於儲存範圍的最小值和最大值。
變數count儲存樹內位於l和h範圍內的BST的數量。初始值為0。
函式getBtreeCount(Btreenode* root, int low, int high, int* count) 獲取BST的根、範圍的左右邊界和count的地址作為引數,並在每次遞迴呼叫時更新count的值。
對於當前根節點,檢查它是否為NULL,如果是,則返回1,因為它不是樹的一部分。
對於當前節點,檢查其所有左子樹和右子樹節點是否位於給定範圍內。透過遞迴呼叫getBtreeCount(root->left, low, high, count); 和 getBtreeCount(root->right, low, high, count);
如果兩個子樹都位於範圍內,並且當前節點也位於範圍內,則當前節點為根的樹位於範圍內。遞增count。if (left && right && root->info >= low && root->info <= high) and ++*count; return 1.
最後,count將具有更新後的值,作為所有子樹的數量。
- 列印count中的結果。
示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A BST node
struct Btreenode {
int info;
Btreenode *left, *right;
};
int getBtreeCount(Btreenode* root, int low, int high, int* count){
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return 1;
int left = getBtreeCount(root->left, low, high, count);
int right = getBtreeCount(root->right, low, high, count);
if (left && right && root->info >= low && root->info <= high) {
++*count;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Btreenode* insert(int data){
Btreenode* temp = new Btreenode;
temp->info = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
int main(){
/* BST for input
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
Btreenode* root = insert(50);
root->left = insert(30);
root->right = insert(70);
root->left->left = insert(20);
root->left->right= insert(40);
root->right->left = insert(60);
root->right->right = insert(80);
int l = 10;
int h = 50;
int count=0;
getBtreeCount(root, l, h, &count);
cout << "Count of subtrees lying in range: " <<count;
return 0;
}輸出
Count of subtrees lying in range: 3


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP