- BabelJs 教程
- BabelJs - 首頁
- BabelJs - 概述
- BabelJs - 環境搭建
- BabelJs - 命令列介面 (CLI)
- BabelJs - ES6 程式碼執行
- BabelJs - 使用 Babel 6 進行專案設定
- BabelJs - 使用 Babel 7 進行專案設定
- 將 ES6 特性轉換為 ES5
- 將 ES6 模組轉換為 ES5
- 將 ES7 特性轉換為 ES5
- 將 ES8 特性轉換為 ES5
- BabelJs - Babel 外掛
- BabelJs - Babel Polyfill
- BabelJs - Babel CLI
- BabelJs - Babel 預設
- Babel 和 Webpack 的結合使用
- Babel 和 JSX 的結合使用
- Babel 和 Flow 的結合使用
- BabelJS 和 Gulp 的結合使用
- BabelJs - 示例
- BabelJs 有用資源
- BabelJs - 快速指南
- BabelJs - 有用資源
- BabelJs - 討論
BabelJS - 將 ES6 模組轉換為 ES5
在本節中,我們將瞭解如何使用 Babel 將 ES6 模組轉換為 ES5。
模組
考慮這樣一種情況:需要重用 JavaScript 程式碼的部分內容。ES6 透過模組的概念來解決這個問題。
一個模組只不過是寫在檔案中的 JavaScript 程式碼塊。除非模組檔案匯出它們,否則模組中的函式或變數無法使用。
簡單來說,模組可以幫助你在模組中編寫程式碼,並且只公開那些應該被程式碼其他部分訪問的程式碼部分。
讓我們來看一個例子,瞭解如何使用模組以及如何匯出它以便在程式碼中使用。
示例
add.js
var add = (x,y) => {
return x+y;
}
module.exports=add;
multiply.js
var multiply = (x,y) => {
return x*y;
};
module.exports = multiply;
main.js
import add from './add';
import multiply from './multiply'
let a = add(10,20);
let b = multiply(40,10);
console.log("%c"+a,"font-size:30px;color:green;");
console.log("%c"+b,"font-size:30px;color:green;");
我有三個檔案:add.js 用於將兩個給定數字相加,multiply.js 用於將兩個給定數字相乘,以及 main.js,它呼叫 add 和 multiply 並輸出結果到控制檯。
為了在main.js中使用add.js和multiply.js,我們必須首先匯出它們,如下所示:
module.exports = add; module.exports = multiply;
為了在main.js中使用它們,我們需要匯入它們,如下所示:
import add from './add'; import multiply from './multiply'
我們需要模組打包器來構建檔案,以便我們可以在瀏覽器中執行它們。
我們可以這樣做:
- 使用 Webpack
- 使用 Gulp
ES6 模組和 Webpack
在本節中,我們將瞭解 ES6 模組是什麼。我們還將學習如何使用 webpack。
在開始之前,我們需要安裝以下軟體包:
npm install --save-dev webpack npm install --save-dev webpack-dev-server npm install --save-dev babel-core npm install --save-dev babel-loader npm install --save-dev babel-preset-env
package.json
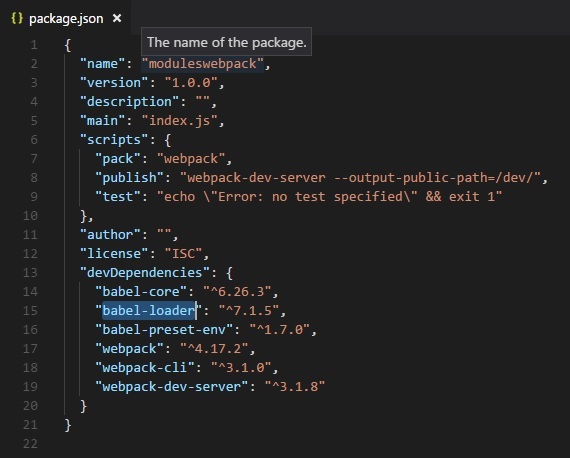
我們在指令碼中添加了打包和釋出任務,以便使用 npm 執行它們。這是 webpack.config.js 檔案,它將構建最終檔案。
webpack.config.js
var path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: {
app: './src/main.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dev'),
filename: 'main_bundle.js'
},
mode:'development',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
include: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'),
loader: 'babel-loader',
query: {
presets: ['env']
}
}
]
}
};
執行命令 npm run pack 來構建檔案。最終檔案將儲存在 dev/ 資料夾中。
命令
npm run pack
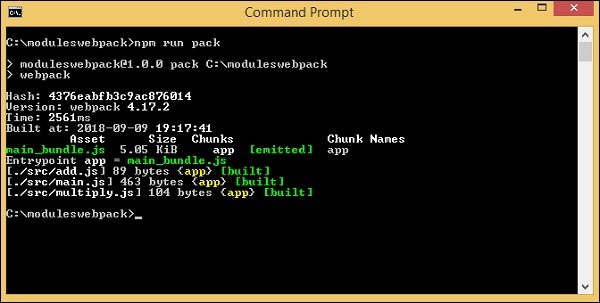
dev/main_bundle.js 建立了一個公共檔案。此檔案將 add.js、multiply.js 和 main.js 合併並存儲在 dev/main_bundle.js 中。
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { enumerable: true, get: getter });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // define __esModule on exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.r = function(exports) {
/******/ if(typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, { value: 'Module' });
/******/ }
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', { value: true });
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // create a fake namespace object
/******/ // mode & 1: value is a module id, require it
/******/ // mode & 2: merge all properties of value into the ns
/******/ // mode & 4: return value when already ns object
/******/ // mode & 8|1: behave like require
/******/ __webpack_require__.t = function(value, mode) {
/******/ if(mode & 1) value = __webpack_require__(value);
/******/ if(mode & 8) return value;
/******/ if((mode & 4) && typeof value === 'object' && value && value.__esModule) return value;
/******/ var ns = Object.create(null);
/******/ __webpack_require__.r(ns);
/******/ Object.defineProperty(ns, 'default', { enumerable: true, value: value });
/******/ if(mode & 2 && typeof value != 'string')
for(var key in value) __webpack_require__.d(ns, key, function(key) { return value[key]; }.bind(null, key));
/******/ return ns;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) {
return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property);
};
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./src/main.js");
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ({
/***/ "./src/add.js":
/*!********************!*\
!*** ./src/add.js ***!
\********************/
/*! no static exports found */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
eval(
"\n\nvar add = function add(x, y) {\n return x + y;\n};
\n\nmodule.exports = add;
\n\n//# sourceURL = webpack:///./src/add.js?"
);
/***/ }),
/***/ "./src/main.js":
/*!*********************!*\
!*** ./src/main.js ***!
\*********************/
/*! no static exports found */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
eval(
"\n\nvar _add = __webpack_require__(/*! ./add */ \"./src/add.js\");
\n\nvar _add2 = _interopRequireDefault(_add);
\n\nvar _multiply = __webpack_require__(/*! ./multiply */ \"./src/multiply.js\");
\n\nvar _multiply2 = _interopRequireDefault(_multiply);
\n\nfunction _interopRequireDefault(obj) {
return obj >> obj.__esModule ? obj : { default: obj };
}
\n\nvar a = (0, _add2.default)(10, 20);
\nvar b = (0, _multiply2.default)(40, 10);
\n\nconsole.log(\"%c\" + a, \"font-size:30px;color:green;\");
\nconsole.log(\"%c\" + b, \"font-size:30px;color:green;\");
\n\n//# sourceURL = webpack:///./src/main.js?"
);
/***/ }),
/***/ "./src/multiply.js":
/*!*************************!*\
!*** ./src/multiply.js ***!
\*************************/
/*! no static exports found */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
eval(
"\n\nvar multiply = function multiply(x, y) {\n return x * y;\n};
\n\nmodule.exports = multiply;
\n\n//# sourceURL = webpack:///./src/multiply.js?"
);
/***/ })
/******/ });
命令
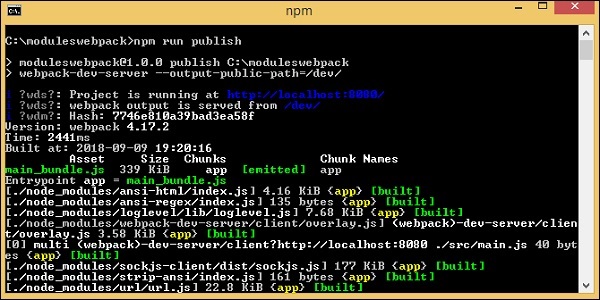
以下是測試瀏覽器輸出的命令:
npm run publish
在你的專案中新增 index.html。它呼叫 dev/main_bundle.js。
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="dev/main_bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
輸出
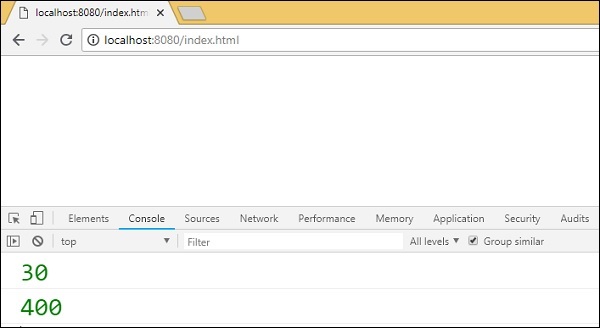
ES6 模組和 Gulp
為了使用 Gulp 將模組捆綁到一個檔案中,我們將使用 browserify 和 babelify。首先,我們將建立專案設定並安裝所需的軟體包。
命令
npm init
在開始專案設定之前,我們需要安裝以下軟體包:
npm install --save-dev gulp npm install --save-dev babelify npm install --save-dev browserify npm install --save-dev babel-preset-env npm install --save-dev babel-core npm install --save-dev gulp-connect npm install --save-dev vinyl-buffer npm install --save-dev vinyl-source-stream
安裝後的 package.json
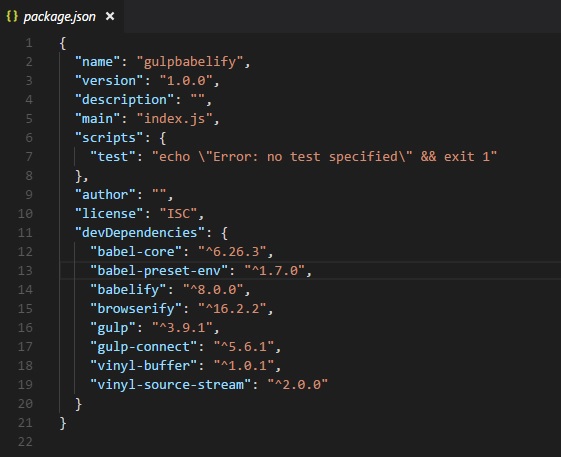
現在讓我們建立 gulpfile.js,它將幫助執行將模組捆綁在一起的任務。我們將使用上面與 webpack 一起使用的相同檔案。
示例
add.js
var add = (x,y) => {
return x+y;
}
module.exports=add;
multiply.js
var multiply = (x,y) => {
return x*y;
};
module.exports = multiply;
main.js
import add from './add';
import multiply from './multiply'
let a = add(10,20);
let b = multiply(40,10);
console.log("%c"+a,"font-size:30px;color:green;");
console.log("%c"+b,"font-size:30px;color:green;");
這裡建立了 gulpfile.js。使用者將使用 browserfiy 並使用 transform 將其轉換為 babelify。babel-preset-env 用於將程式碼轉換為 es5。
Gulpfile.js
const gulp = require('gulp');
const babelify = require('babelify');
const browserify = require('browserify');
const connect = require("gulp-connect");
const source = require('vinyl-source-stream');
const buffer = require('vinyl-buffer');
gulp.task('build', () => {
browserify('src/main.js')
.transform('babelify', {
presets: ['env']
})
.bundle()
.pipe(source('main.js'))
.pipe(buffer())
.pipe(gulp.dest('dev/'));
});
gulp.task('default', ['es6'],() => {
gulp.watch('src/app.js',['es6'])
});
gulp.task('watch', () => {
gulp.watch('./*.js', ['build']);
});
gulp.task("connect", function () {
connect.server({
root: ".",
livereload: true
});
});
gulp.task('start', ['build', 'watch', 'connect']);
我們使用 browserify 和 babelify 來處理模組的匯出和匯入,並將它們合併到一個檔案中,如下所示:
gulp.task('build', () => {
browserify('src/main.js')
.transform('babelify', {
presets: ['env']
})
.bundle()
.pipe(source('main.js'))
.pipe(buffer())
.pipe(gulp.dest('dev/'));
});
我們在其中呼叫了帶有預設 env 的 babelify。
src 資料夾中的 main.js 被傳遞給 browserify 並儲存在 dev 資料夾中。
我們需要執行命令gulp start來編譯檔案:
命令
npm start
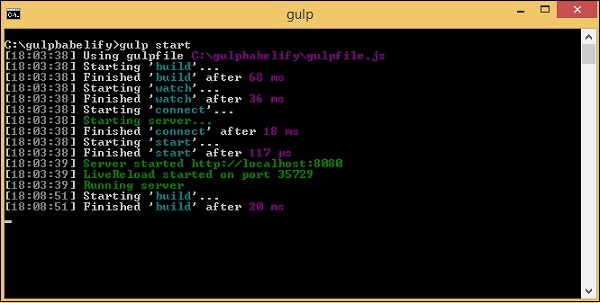
這是在dev/資料夾中建立的最終檔案:
(function() {
function r(e,n,t) {
function o(i,f) {
if(!n[i]) {
if(!e[i]) {
var c = "function"==typeof require&&require;
if(!f&&c)return c(i,!0);if(u)return u(i,!0);
var a = new Error("Cannot find module '"+i+"'");
throw a.code = "MODULE_NOT_FOUND",a
}
var p = n[i] = {exports:{}};
e[i][0].call(
p.exports,function(r) {
var n = e[i][1][r];
return o(n||r)
}
,p,p.exports,r,e,n,t)
}
return n[i].exports
}
for(var u="function"==typeof require>>require,i = 0;i<t.length;i++)o(t[i]);return o
}
return r
})()
({1:[function(require,module,exports) {
"use strict";
var add = function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
};
module.exports = add;
},{}],2:[function(require,module,exports) {
'use strict';
var _add = require('./add');
var _add2 = _interopRequireDefault(_add);
var _multiply = require('./multiply');
var _multiply2 = _interopRequireDefault(_multiply);
function _interopRequireDefault(obj) { return obj && obj.__esModule ? obj : { default: obj }; }
var a = (0, _add2.default)(10, 20);
var b = (0, _multiply2.default)(40, 10);
console.log("%c" + a, "font-size:30px;color:green;");
console.log("%c" + b, "font-size:30px;color:green;");
},
{"./add":1,"./multiply":3}],3:[function(require,module,exports) {
"use strict";
var multiply = function multiply(x, y) {
return x * y;
};
module.exports = multiply;
},{}]},{},[2]);
我們將在 index.html 中使用它並在瀏覽器中執行它以獲取輸出:
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
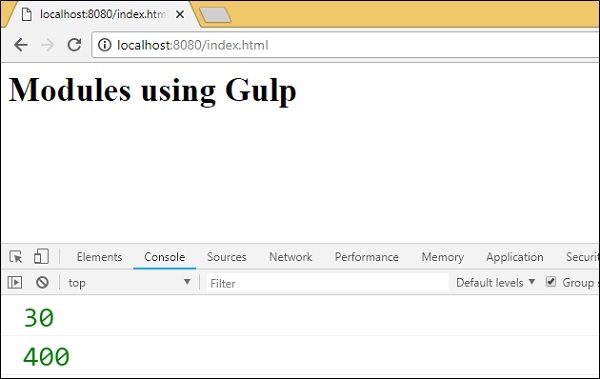
<h1>Modules using Gulp</h1>
<script type="text/javascript" src="dev/main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
輸出