什麼是朗伯余弦定律?(照明定律)
任何表面接收到的光線取決於該表面的法線與光通量之間的夾角。朗伯余弦定律解釋了表面照度與角度餘弦之間的關係。
說明
朗伯余弦照明定律指出:
“表面的照度與其法線與入射光方向之間夾角的餘弦成正比”。
也就是說,
$$\mathrm{\mathit{E}\propto cos\, \theta \: \: \: \cdot \cdot \cdot \left ( 1 \right )}$$
解釋
情況一 – 考慮一個垂直於光通量的表面,如圖1所示。
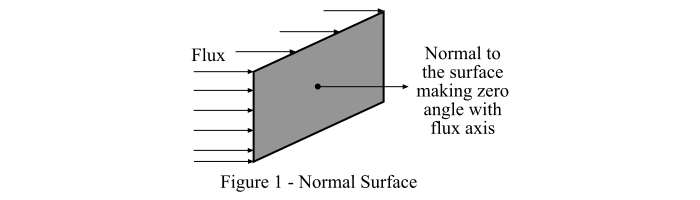
然後,根據朗伯余弦定律,我們得到:
$$\mathrm{照度,\mathit{E}=\frac{\phi }{\mathit{A}}\: \: \: \cdot \cdot \cdot \left ( 2 \right )}$$
情況二 – 考慮一個相對於光通量傾斜的表面,該表面的法線與光通量軸線成一個角度 (θ),如圖2所示。
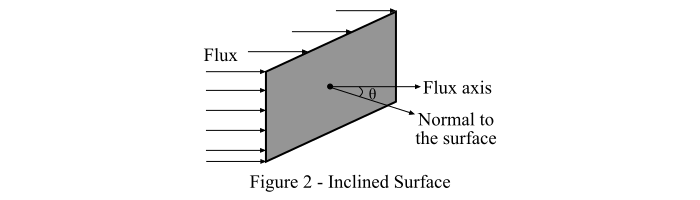
然後,根據朗伯余弦定律,我們得到:
$$\mathrm{\mathit{E}=\frac{\phi }{\mathit{A}}\times cos\, \theta \: \: \: \cdot \cdot \cdot \left ( 3 \right )}$$
情況三 – 考慮平面表面上的一個點 'P',光源 (S) 與點 'P' 之間的距離為 'r' 米。光源 (S) 位於距表面 'h' 米的高度,其發光強度為 'I' 坎德拉,如圖3所示。
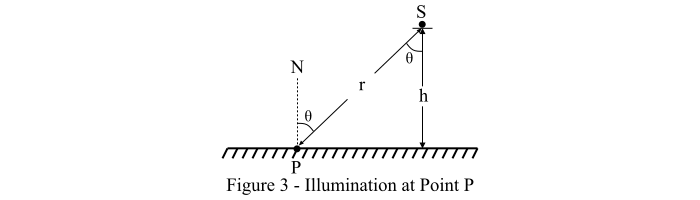
然後,根據餘弦照明定律,我們得到點 'P' 的照度為:
$$\mathrm{\mathit{E_{P}}=\mathit{\frac{I }{r^{\mathrm{2}}}}\times cos\, \theta}$$
從圖3,我們有:
$$\mathrm{cos\, \theta \: =\: \mathit{\frac{h}{r}}}$$
$$\mathrm{\Rightarrow \mathit{r} \: =\: \frac{\mathit{h}}{cos\, \theta}}$$
因此,點 'P' 的照度為:
$$\mathrm{\mathit{E_{P}}\: =\: \mathit{\frac{I }{\left ( \mathit{h}/\mathrm{cos\, \theta }\right )^{\mathrm{2}}}}\times cos\, \theta}$$
$$\mathrm{\therefore \mathit{E_{P}}\: =\: \mathit{\frac{I }{\mathit{h}^{\mathrm{2}}}}\times cos^{3}\, \theta\: \: \: \cdot \cdot \cdot \left ( 4 \right )}$$
其中,I/h2 是位於光源正下方的任何點的照度。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP