SVM中的分離平面
支援向量機 (SVM) 是一種廣泛應用於手寫識別、情感分析等領域的監督學習演算法。為了分離不同的類別,SVM 計算最優超平面,該超平面或多或少準確地在兩個類別之間建立了一個邊界。
以下是一些在 SVM 中分離超平面的方法。
資料預處理 - SVM 需要經過標準化、縮放和中心化處理的資料,因為它們對這些特徵敏感。
選擇核函式 - 核函式用於將輸入轉換為更高維的空間。其中一些包括線性核、多項式核和徑向基函式。
讓我們考慮 SVM 超平面可以區分的兩種情況。
線性可分情況。
非線性可分情況。
示例 1
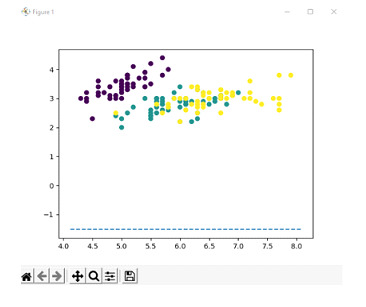
對於線性可分情況,讓我們考慮具有二維特徵的鳶尾花資料集。線性可分情況是指特徵可以透過超平面線性分離。鳶尾花資料集是展示線性可分超平面的一個很好的初學者友好方法。目標是顯示一個本質上是線性的超平面。
演算法
匯入所有庫
載入鳶尾花資料集,並將資料和目標特徵分別分配給變數 x 和 y。
使用 train_test_split 函式,為 x_train、x_test、y_train 和 y_test 分配值。
使用線性核構建 SVM 模型,並根據訓練資料點擬合模型。
預測標籤並列印模型的準確率。
使用模型將模型的權重和偏置分別作為模型的係數和直線的截距。
使用權重和偏置計算斜率和 y 截距。
在圖表中繪製資料點並展示它。
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tts
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
iris=datasets.load_iris()
x=iris.data
y=iris.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = tts(x,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=10)
#build an SVM model with linear kernel
clf=SVC(kernel='linear')
#fit the model
clf.fit(x_train,y_train)
#predict the labels
y_pred=clf.predict(x_test)
#calculate the accuracy
acc=accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
print("Accuracy: ", acc)
#get the hyperplane parameters
w=clf.coef_[0]
b=clf.intercept_[0]
#calculate the slope and intercept
slope = -w[0]/w[1]
y_int = -b/w[1]
#plot the dataset and hyperplane
plt.scatter(x[:,0], x[:,1], c=y)
axes=plt.gca()
x_vals=np.array(axes.get_xlim())
y_vals=y_int+slope*x_vals
plt.plot(x_vals, y_vals, '--')
plt.show()
我們將資料集分成訓練集和測試集,其中測試集佔總資料的 30%。然後,我們建立一個具有線性核的 SVM 分類器,並將模型擬合到訓練資料。
我們預測測試資料的標籤,並將獲得的結果儲存在單獨的變數中,透過將預測值與真實值進行比較來計算模型的準確率,並列印獲得的準確率,即 1.0。
然後從訓練資料集檢索超平面的引數,並計算超平面的斜率和截距,然後使用散點圖繪製,每個類別使用不同的顏色。
Accuracy: 1.0
輸出
示例 2
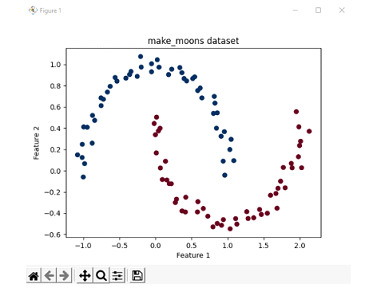
考慮一個案例不線性可分的情況。在這種情況下,我們使用 scikit-learn 庫中提供的 make_moons 資料集。make_moons 資料集是展示 2 個或多個類別不線性可分情況的好方法。因此,此示例用於描述非線性可分情況。
讓我們首先列印資料集的資料點,以便了解我們正在處理什麼。
演算法
匯入所有必要的庫。
使用 100 個樣本生成 make_moons 資料集,並具有最小的噪聲水平。
在圖表中繪製這些資料點並列印,並將顏色圖設定為紅色和藍色。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
# Generate the make_moons dataset with 100 samples and a noise level of 0.05
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=100, noise=0.05, random_state=42)
# To show the dataset
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
# Set the plot labels and title
plt.xlabel('Feature 1')
plt.ylabel('Feature 2')
plt.title('make_moons dataset')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
輸出
演算法
匯入程式中使用的所有庫
從 make_moons 資料集中生成 100 個數據樣本,噪聲儘可能低。
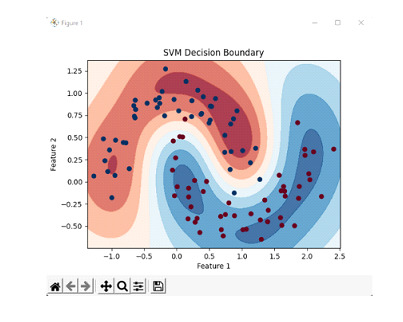
使用徑向基函式 (RBF) 核初始化 SVC 分類器,並根據分類器訓練資料點。
根據資料點,將前面初始化的分類器擬合到資料集。
查詢資料中特徵和標籤的最大值和最小值。
使用上述值,使用 linspace 函式構造網格。
要返回網格的一維表示,應用 ravel 函式並使用 np.c_ 沿第二軸切片。
要定義決策邊界,建立決策邊界的等高線圖。
列印影像和標籤。
示例
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# load moons dataset
x, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=100, noise=0.15, random_state=42)
# create an SVM classifier implementing RBF kernel
clf = SVC(kernel='rbf', gamma=2)
# train the classifier on the dataset
clf.fit(X, y)
# create a meshgrid representing features and labels
x_min, x_max = x[:, 0].min() - 0.1, x[:, 0].max() + 0.1
y_min, y_max = x[:, 1].min() - 0.1, x[:, 1].max() + 0.1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, 500), np.linspace(y_min, y_max, 500))
z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
z = z.reshape(xx.shape)
# create a contour plot of the decision boundary
plt.contourf(xx, yy, z, cmap=plt.cm.RdBu, alpha=0.8)
plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
# set the plot labels and title
plt.xlabel('Feature 1')
plt.ylabel('Feature 2')
plt.title('SVM Decision Boundary')
# show the plot
plt.show()
我們透過建立 100 個樣本(噪聲級別為 0.15,隨機種子為 42)生成資料集,並建立一個 SVM 分類器,並在資料集上訓練分類器。然後,我們定義一組點來表示特徵和標籤。然後,我們計算這些點的決策函式值,並將其重新整形以匹配網格的維度。然後,我們建立決策邊界的等高線圖,其中決策函式值決定區域的顏色。我們還繪製原始資料點,不同顏色代表不同類別。
輸出
結論
支援向量機是更廣泛使用的演算法之一,用於各種領域,主要是文字和語音分類,或 NLP 中的情感分析。它在分類方面的多功能性使其成為更受歡迎的演算法之一。
在其他情況下,它有其自身的缺點。有時,SVM 在計算上可能非常密集,並且由於模型的敏感性,需要仔細檢查提供給模型的資料。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP