圖及其遍歷演算法
在本節中,我們將瞭解圖資料結構以及其遍歷演算法。
圖是一種非線性資料結構,由一些節點及其連線的邊組成。邊可以是有向的或無向的。該圖可以表示為 G(V, E)。以下圖可以表示為 G({A, B, C, D, E}, {(A, B), (B, D), (D, E), (B, C), (C, A)})
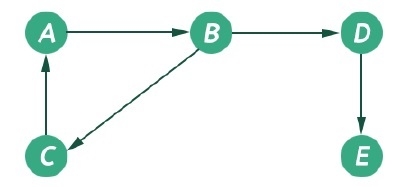
圖具有兩種型別的遍歷演算法。它們被稱為廣度優先搜尋和深度優先搜尋。
廣度優先搜尋 (BFS)
廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 遍歷是一種用於訪問給定圖的所有節點的演算法。在這個遍歷演算法中,選擇一個節點,然後逐個訪問所有相鄰節點。在完成所有相鄰頂點後,它會繼續檢查另一個頂點並再次檢查其相鄰頂點。
演算法
bfs(vertices, start) Input: The list of vertices, and the start vertex. Output: Traverse all of the nodes, if the graph is connected. Begin define an empty queue que at first mark all nodes status as unvisited add the start vertex into the que while que is not empty, do delete item from que and set to u display the vertex u for all vertices 1 adjacent with u, do if vertices[i] is unvisited, then mark vertices[i] as temporarily visited add v into the queue mark done mark u as completely visited done End
深度優先搜尋 (DFS)
深度優先搜尋 (DFS) 是一種圖遍歷演算法。在這個演算法中,給定一個起始頂點,當找到一個相鄰頂點時,它會首先移動到該相鄰頂點並嘗試以相同的方式進行遍歷。
演算法
dfs(vertices, start) Input: The list of all vertices, and the start node. Output: Traverse all nodes in the graph. Begin initially make the state to unvisited for all nodes push start into the stack while stack is not empty, do pop element from stack and set to u display the node u if u is not visited, then mark u as visited for all nodes i connected to u, do if ith vertex is unvisited, then push ith vertex into the stack mark ith vertex as visited done done End

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP