查詢C++中從源點出髮長度大於k的路徑
概念
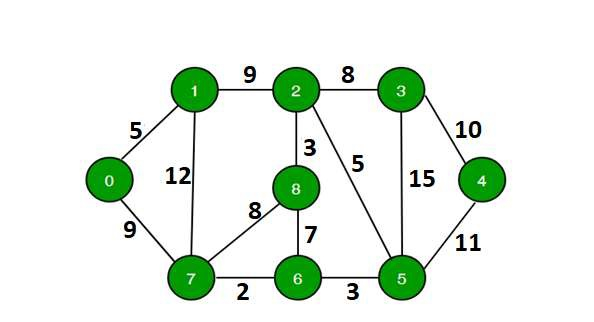
對於給定的圖,圖中的源頂點和一個數字k(這裡k表示源頂點和目標頂點之間圖的路徑長度),我們的任務是確定是否存在從給定源點開始到任何其他頂點(即目標頂點)結束的簡單路徑(沒有任何環路)。圖如下所示:
輸入
Source s = 0, k = 64
輸出
True
存在一條簡單路徑0 -> 7 -> 1 -> 2 -> 8 -> 6 -> 5 -> 3 -> 4,總距離為68公里,大於64。
輸入
Source s = 0, k = 70
輸出
False
在上圖中,最長的簡單路徑距離為69(0 -> 7 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8),因此對於任何大於69的輸入,輸出都應為false。
方法
需要注意的是,簡單的執行廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 或深度優先搜尋 (DFS) 並選擇每一步的最長邊是行不通的。原因是較短的邊可以透過連線到它的權重較高的邊產生更長的路徑。
現在,核心概念是實現回溯演算法。在這種情況下,我們從給定的源點開始;遍歷當前頂點的所有路徑。在這裡,我們跟蹤當前與源點的距離。如果距離超過k,則返回true。但是,如果路徑沒有產生超過k的距離,則我們回溯。
現在的問題是如何確保路徑是簡單的,並且我們不會迴圈進入一個環路?這裡,核心概念是使用一個數組跟蹤當前路徑的頂點。在這種情況下,每當我們向路徑新增一個頂點時,我們都驗證它是否已經存在於當前路徑中。如果存在,則忽略該邊。
示例
// Program to find if there is a simple path with
// weight more than k
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// iPair ==> Integer Pair
typedef pair<int, int> iPair;
// Now this class represents a dipathted graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph{
int V1; // Indicates no. of vertices
// In this case, in a weighted graph, we need to store vertex
// and weight pair for every edge
list< pair<int, int>> *adj1;
bool pathMoreThanKUtil(int src1, int k, vector<bool>&path1);
public:
Graph(int V1); // Shows constructor
// Shows function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int u1, int v1, int w1);
bool pathMoreThanK(int src1, int k);
};
// Used to return true if graph has path more than k length
bool Graph::pathMoreThanK(int src1, int k){
// Used to create a path array with nothing included
// in path
vector<bool> path1(V1, false);
// Used to add source vertex to path
path1[src1] = 1;
return pathMoreThanKUtil(src1, k, path1);
}
// Used to print shortest paths from src to all other vertices
bool Graph::pathMoreThanKUtil(int src1, int k, vector<bool>&path1){
// Now if k is 0 or negative, return true;
if (k <= 0)
return true;
//Used to get all adjacent vertices of source vertex src and
// recursively explore all paths from src.
list<iPair>::iterator i;
for (i = adj1[src1].begin(); i != adj1[src1].end(); ++i){
// Used to get adjacent vertex and weight of edge
int v1 = (*i).first;
int w1 = (*i).second;
// Now if vertex v is already there in path, then
// there is a cycle (we ignore this edge)
if (path1[v1] == true)
continue;
// Now if weight of is more than k, return true
if (w1 >= k)
return true;
// Else add this vertex to path
path1[v1] = true;
// Now if this adjacent can provide a path longer
// than k, return true.
if (pathMoreThanKUtil(v1, k-w1, path1))
return true;
// Backtrack
path1[v1] = false;
}
// Now if no adjacent could produce longer path, return
// false
return false;
}
// Used to allocates memory for adjacency list
Graph::Graph(int V1){
this->V1 = V1;
adj1 = new list<iPair> [V1];
}
//Shows utility function to an edge (u, v) of weight w
void Graph::addEdge(int u1, int v1, int w1){
adj1[u1].push_back(make_pair(v1, w1));
adj1[v1].push_back(make_pair(u1, w1));
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main(){
// Used to create the graph given in above fugure
int V1 = 9;
Graph g(V1);
// making above shown graph
g.addEdge(0, 1, 5);
g.addEdge(0, 7, 9);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(1, 7, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 8);
g.addEdge(2, 8, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 10);
g.addEdge(3, 4, 10);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 15);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 11);
g.addEdge(5, 6, 3);
g.addEdge(6, 7, 2);
g.addEdge(6, 8, 7);
g.addEdge(7, 8, 8);
int src1 = 0;
int k = 70;
g.pathMoreThanK(src1, k)? cout << "Yes\n" :
cout << "No\n";
k = 68;
g.pathMoreThanK(src1, k)? cout << "Yes\n" :
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}輸出
No Yes

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP