用C語言解釋連結串列中元素的插入
連結串列使用動態記憶體分配,即它們會根據需要增長和縮小。它們被定義為節點的集合。在這裡,節點有兩個部分,分別是資料和連結。資料、連結和連結串列的表示如下:
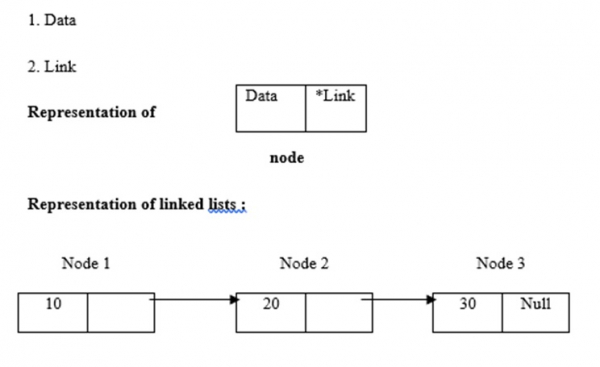
連結串列操作
在C語言中,連結串列有三種操作,如下:
- 插入
- 刪除
- 遍歷
插入
舉個例子,我們在節點2和節點3之間插入節點5。
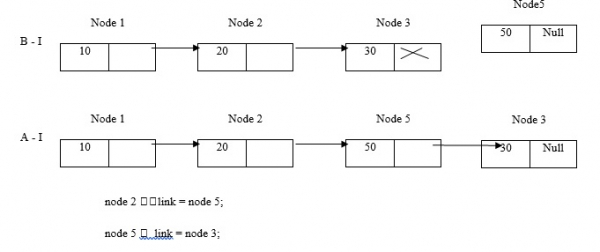
現在,在開頭插入節點5。
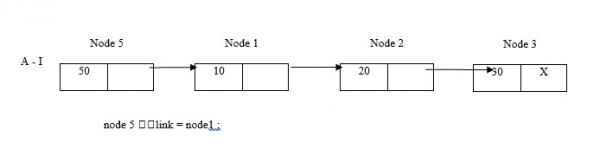
在末尾插入節點5。
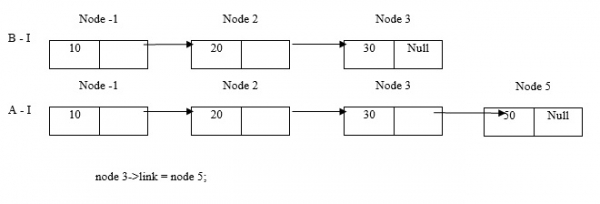
在末尾插入節點5。
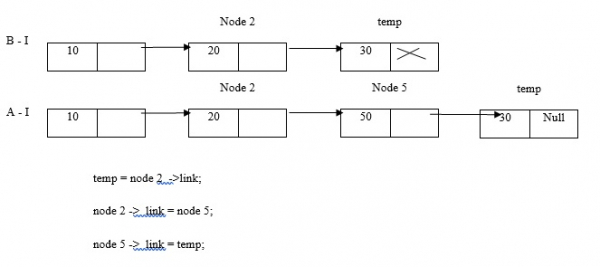
注意
- 由於節點沒有命名,我們無法在節點2之前插入節點5。
- 如果給出其位置,我們可以將節點5插入到2之前。
C程式,用於在連結串列中插入元素
以下是用於在連結串列中插入元素的C程式:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
int val;
struct node *next;
};
void print_list(struct node *head){
printf("H->");
while(head){
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("……
");
}
void insert_front(struct node **head, int value){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL){
printf(" Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
void insert_end(struct node **head, int value){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
struct node * last = NULL;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL){
printf(" Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
new_node->next = NULL;
if( *head == NULL){
*head = new_node;
return;
}
last = *head;
while(last->next) last = last->next;
last->next = new_node;
}
void insert_after(struct node *head, int value, int after){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
struct node *tmp = head;
while(tmp) {
if(tmp->val == after) { /*found the node*/
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL) {
printf("Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
new_node->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = new_node;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
void insert_before(struct node **head, int value, int before){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
struct node * tmp = *head;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL){
printf("Out of memory");
return;
}
new_node->val = value;
if((*head)->val == before){
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
return;
}
while(tmp && tmp->next) {
if(tmp->next->val == before) {
new_node->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = new_node;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
/*Before node not found*/
free(new_node);
}
void main(){
int count = 0, i, val, after, before;
struct node * head = NULL;
printf("Enter no: of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++){
printf("Enter %dth element: ", i);
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_front(&head, val);
}
printf("starting list: ");
print_list(head);
printf("enter front element: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_front(&head, val);
printf("items after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
printf("enter last element: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_end(&head, val);
printf("items after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
printf("Enter an ele to insert in the list: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
printf("Insert after: ");
scanf("%d", &after);
insert_after(head, val, after);
printf("List after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
printf("Enter an ele to insert in the list: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
printf("Insert before: ");
scanf("%d", &before);
insert_before(&head, val, before);
printf("List after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
}輸出
執行上述程式後,會產生以下結果:
Enter no: of elements: 4 Enter 0th element: 1 Enter 1th element: 2 Enter 2th element: 3 Enter 3th element: 4 starting list: H->4->3->2->1->...... enter front element: 5 items after insertion: H->5->4->3->2->1->...... enter last element: 0 items after insertion: H->5->4->3->2->1->0->...... Enter an ele to insert in the list: 6 Insert after: 0 List after insertion: H->5->4->3->2->1->0->6->...... Enter an ele to insert in the list: 7 Insert before: 5 List after insertion: H->7->5->4->3->2->1->0->6->......

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP