使用連結串列實現優先佇列 (C語言)
給定資料和優先順序(整數),任務是根據給定的優先順序建立一個連結串列並顯示結果。
佇列是一種先進先出 (FIFO) 資料結構,其中最先插入的元素也是最先被刪除的元素。優先佇列是一種佇列,其中元素的插入和刪除取決於優先順序。它可以使用佇列、棧或連結串列資料結構來實現。優先佇列的實現遵循以下規則:
- 具有最高優先順序的數 據或元素將優先於具有最低優先順序的數 據或元素執行。
- 如果兩個元素具有相同的優先順序,則它們將按照新增到列表中的順序執行。
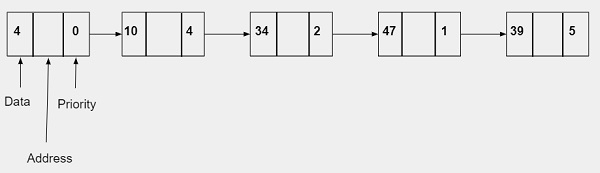
用於實現優先佇列的連結串列節點將包含三個部分:
- 資料 - 它將儲存整數值。
- 地址 - 它將儲存下一個節點的地址。
- 優先順序 - 它將儲存優先順序,這是一個整數值。它的範圍可以是 0-10,其中 0 代表最高優先順序,10 代表最低優先順序。
示例
輸入
輸出

演算法
Start Step 1-> Declare a struct node Declare data, priority Declare a struct node* next Step 2-> In function Node* newNode(int d, int p) Set Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)) Set temp->data = d Set temp->priority = p Set temp->next = NULL Return temp Step 3-> In function int peek(Node** head) return (*head)->data Step 4-> In function void pop(Node** head) Set Node* temp = *head Set (*head) = (*head)->next free(temp) Step 5-> In function push(Node** head, int d, int p) Set Node* start = (*head) Set Node* temp = newNode(d, p) If (*head)->priority > p then, Set temp->next = *head Set (*head) = temp Else Loop While start->next != NULL && start->next->priority < p Set start = start->next Set temp->next = start->next Set start->next = temp Step 6-> In function int isEmpty(Node** head) Return (*head) == NULL Step 7-> In function int main() Set Node* pq = newNode(7, 1) Call function push(&pq, 1, 2) Call function push(&pq, 3, 3) Call function push(&pq, 2, 0) Loop While (!isEmpty(&pq)) Print the results obtained from peek(&pq) Call function pop(&pq) Stop
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// priority Node
typedef struct node {
int data;
int priority;
struct node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int d, int p) {
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = d;
temp->priority = p;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
int peek(Node** head) {
return (*head)->data;
}
void pop(Node** head) {
Node* temp = *head;
(*head) = (*head)->next;
free(temp);
}
void push(Node** head, int d, int p) {
Node* start = (*head);
Node* temp = newNode(d, p);
if ((*head)->priority > p) {
temp->next = *head;
(*head) = temp;
} else {
while (start->next != NULL &&
start->next->priority < p) {
start = start->next;
}
// Either at the ends of the list
// or at required position
temp->next = start->next;
start->next = temp;
}
}
// Function to check the queue is empty
int isEmpty(Node** head) {
return (*head) == NULL;
}
// main function
int main() {
Node* pq = newNode(7, 1);
push(&pq, 1, 2);
push(&pq, 3, 3);
push(&pq, 2, 0);
while (!isEmpty(&pq)) {
printf("%d ", peek(&pq));
pop(&pq);
}
return 0;
}輸出
2 7 1 3

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP