檢查無向圖中節點 S 和 T 之間是否存在僅 S 和 T 重複的環路
介紹
圖是一種強大的數學結構,允許我們對各種實體之間的關係進行建模和視覺化。在計算機科學中,圖在各種演算法和資料結構中都有應用。無向圖的一個常見問題是確定兩個給定節點之間是否存在環路。在本文中,我們將著手解決這個難題,並使用 C/C++ 提供一個優雅的解決方案。確定無向圖中的環路對於各種連線性很重要的應用至關重要。
無向圖是確定兩個給定節點之間是否存在環路
無權雙向(或無向)圖由透過邊連線的頂點或節點組成。這些邊沒有分配任何特定的權重或距離,而是僅指示存在連線,沒有任何方向偏差。
路徑表示一系列互連的頂點,其中每個頂點都透過邊直接與其相鄰的對應頂點連線。在這裡,我們專注於查詢連線兩個不同頂點(明確稱為源節點和目標節點)的路徑,並具有最小的總邊遍歷次數。
考慮一個無向圖,其中每條邊表示兩個節點之間的連線。我們的目標是確定在這個圖中是否存在連線節點 S 和節點 T 的環路,當這兩個節點都可以在任何路徑中重複出現。
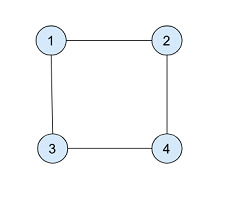
在上圖中,它有四個頂點和 3 條邊,我們需要檢查節點 1 和節點 4 之間是否存在環路。DFS 演算法從節點 1(源節點)開始,訪問其相鄰節點 - 節點 2 和節點 3。然後它訪問節點 4,該節點之前已被節點 3 訪問過。由於節點 4 不是節點 3 的父節點,因此圖中存在環路。
方法 1:C++ 程式,用於檢查無向圖中節點 S 和 T 之間是否存在僅 S 和 T 重複的環路
為了有效地解決這個問題,我們將採用深度優先搜尋 (DFS),這是一種廣泛使用的圖遍歷演算法。DFS 背後的基本思想是儘可能沿著每個分支向下探索,然後再回溯。
演算法
步驟 1 − 它使用一個 `Graph` 類來封裝圖的屬性。
步驟 2 − 它包括諸如 `addEdge()`(連線兩個頂點)、`hasCycle()`(確定兩個節點之間是否存在環路)以及用於 DFS 遍歷的內部輔助方法(例如 `dfsUtil()`)之類的函式。
步驟 3 − 在驅動程式程式碼 (`main()` )中,我們提示使用者輸入圖中的頂點數和邊數。
步驟 4 − 然後逐一詢問邊對(節點連線)。
步驟 5 − 最後,詢問源頂點和目標頂點。
步驟 6 − 程式將輸出這兩個節點之間是否存在可能重複的路徑。
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Graph class representing our underlying structure
class Graph {
int numNodes; // Total number of nodes in the graph
vector<vector<int>> adjList; // Adjacency list representation
public:
// Constructor taking input parameter specifying the total number of nodes
Graph(int n) {
numNodes = n;
adjList.resize(n);
}
// Function allowing adding edges between two vertices u and v (0-based indexing)
void addEdge(int u, int v) {
adjList[u].push_back(v);
adjList[v].push_back(u);
}
private:
// Utility function used by hasCycle() to perform DFS search recursively starting from vertex s.
// It returns true if the cycle is found during exploration.
bool dfsUtil(int s, bool visited[], bool parent[]) {
visited[s] = true;
for (int v : adjList[s]) {
if (!visited[v]) {
parent[v] = true;
// Recursive call
if (dfsUtil(v, visited, parent))
return true;
}
else if(parent[v])
return true;
}
return false;
}
public:
// Function that checks whether a cycle exists between nodes S and T.
bool hasCycle(int s, int t) {
bool* visited = new bool[numNodes];
bool* parent = new bool[numNodes];
for(int i=0; i<numNodes; ++i){
visited[i]=false;
parent[i]=false;
}
parent[s] = true;
if(dfsUtil(s, visited, parent)){
delete[] visited;
delete[] parent;
return dfsUtil(t,visited,parent);
}
delete[] visited;
return false;
}
};
int main() {
int numVertices = 4;
int numEdges = 4;
Graph graph(numVertices);
vector<pair<int,int>> edges = {{1,2},{2,3},{3,4},{4,1}};
for(auto edge : edges){
int u = edge.first - 1;
int v = edge.second - 1;
graph.addEdge(u,v);
}
int source = 1 - 1;
int target = 4 - 1;
if(graph.hasCycle(source,target))
cout<<"A cycle exists between node "<< source+1 <<" and node " <<target+1<<".";
else
cout<<"No cycle found between node "<< source+1<<" and node " <<target + 1<<".";
return 0;
}
輸出
A cycle exists between node 1 and node 4.
結論
當可以透過在不同路徑上重複特定節點來形成環路時,這個問題變得更加有趣。透過利用深度優先搜尋 (DFS),我們已經成功開發出健壯的 C++ 程式碼,該程式碼包含用於探索圖的解決方案,同時有效地檢查連線所選節點 S 和 T 的重複項的環路是否存在。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP