C++ 中 K 站點內最便宜的航班
假設我們有 n 個城市由 m 個航班連線。每次航班從 u 出發到達 v,價格為 w。如果我們擁有所有城市和航班,以及起始城市 src 和目的地 dst,我們的任務是在最多 k 站點的限制下找到從 src 到 dst 的最便宜價格。如果沒有這樣的路線,則返回 -1。
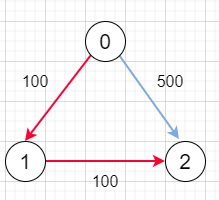
因此,如果輸入類似於 n = 3,edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]],src = 0,dst = 2,k = 1,則輸出將為 200
為了解決這個問題,我們將遵循以下步驟:
建立一個名為 Data 的資料結構,它可以儲存節點、距離和值
定義一個二維陣列 cost
cost := 一個 (n + 1) x (K + 10) 階的二維陣列,用無窮大填充
定義一個三維陣列 graph
對於初始化 i := 0,當 i < flights 的大小,更新 (增加 i):
u := flights[i, 0]
v := flights[i, 1]
在 graph[u] 的末尾插入 { v, flights[i, 2] }
定義一個優先順序佇列 q
將 Data(src, 0, 0) 插入 q
cost[src, 0] := 0
ans := -1
當 (q 不為空) 時:
temp := q 的頂部元素
curr := temp.node
從 q 中刪除元素
dist := temp.dist
如果 curr 與 dst 相同,則:
返回 temp.cost
(增加 dist)
如果 dist > K + 1,則:
忽略以下部分,跳過到下一次迭代
對於初始化 i := 0,當 i < graph[curr] 的大小,更新 (增加 i):
neighbour := graph[curr, i, 0]
如果 cost[neighbour, dist] > cost[curr, dist - 1] + graph[curr, i, 1],則:
cost[neighbour, dist] := cost[curr, dist - 1] + graph[curr, i, 1]
將 Data(neighbour, dist, cost[neighbour, dist]) 插入 q
返回 -1
示例
讓我們看看以下實現以獲得更好的理解:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Data{
int node, dist, cost;
Data(int a, int b, int c){
node = a;
dist = b;
cost = c;
}
};
struct Comparator{
bool operator() (Data a, Data b) {
return !(a.cost < b.cost);
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> cost;
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
cost = vector<vector<int> >(n + 1, vector<int>(K + 10, INT_MAX));
vector<vector<int> > graph[n];
for (int i = 0; i < flights.size(); i++) {
int u = flights[i][0];
int v = flights[i][1];
graph[u].push_back({ v, flights[i][2] });
}
priority_queue<Data, vector<Data>, Comparator> q;
q.push(Data(src, 0, 0));
cost[src][0] = 0;
int ans = -1;
while (!q.empty()) {
Data temp = q.top();
int curr = temp.node;
q.pop();
int dist = temp.dist;
if (curr == dst)
return temp.cost;
dist++;
if (dist > K + 1)
continue;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[curr].size(); i++) {
int neighbour = graph[curr][i][0];
if (cost[neighbour][dist] > cost[curr][dist - 1] + graph[curr][i][1]) {
cost[neighbour][dist] = cost[curr][dist - 1] + graph[curr][i][1];
q.push(Data(neighbour, dist, cost[neighbour][dist]));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
main(){
Solution ob;
vector<vector<int>> v = {{0,1,100},{1,2,100},{0,2,500}};
cout << (ob.findCheapestPrice(3, v, 0, 2, 1));
}輸入
3, {{0,1,100},{1,2,100},{0,2,500}}, 0, 2, 1輸出
200


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP