C 語言實現迴圈排程演算法
給定 n 個程序及其對應的突發時間和時間片,任務是找到平均等待時間和平均週轉時間並顯示結果。
什麼是迴圈排程演算法?
迴圈排程是一種 CPU 排程演算法,專門為分時系統設計。它類似於先來先服務 (FCFS) 排程演算法,但有一點不同:在迴圈排程中,程序會受到時間片大小的限制。一個時間單位稱為時間片或時間量子。時間片可以從 10 到 100 毫秒不等。CPU 將就緒佇列視為一個迴圈佇列,以給定的時間片執行程序。它遵循搶佔式方法,因為會為程序分配固定時間。它的唯一缺點是上下文切換的開銷。
我們需要計算什麼?
**完成時間**是程序完成執行所需的時間。
**週轉時間**是程序提交到完成之間的時間間隔。
週轉時間 = 程序完成時間 – 程序提交時間
等待時間是週轉時間和突發時間之間的差值。
等待時間 = 週轉時間 – 突發時間
示例
給定 3 個程序 P1、P2 和 P3,其對應的突發時間分別為 24、3 和 3。
| 程序 | 突發時間 |
|---|---|
| P1 | 24 |
| P2 | 3 |
| P3 | 3 |
由於時間片為 4 毫秒,程序 P1 獲得前 4 毫秒,但它還需要另外 20 毫秒才能完成執行,但 CPU 將在第一個時間片後搶佔它,並將 CPU 分配給下一個程序 P2。如表所示,程序 P2 僅需 3 毫秒即可完成執行,因此 CPU 將僅分配 3 毫秒的時間片,而不是 4 毫秒。
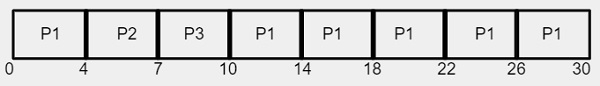
使用甘特圖,平均等待時間計算如下:
平均等待時間 = 17/3 = 5.66 毫秒
演算法
Start
Step 1-> In function int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int tat[])
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i]
return 1
Step 2-> In function int waitingtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int quantum)
Declare rem_bt[n]
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set rem_bt[i] = bt[i]
Set t = 0
Loop While (1)
Set done = true
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
If rem_bt[i] > 0 then,
Set done = false
If rem_bt[i] > quantum then,
Set t = t + quantum
Set rem_bt[i] = rem_bt[i] - quantum
Else
Set t = t + rem_bt[i]
Set wt[i] = t - bt[i]
Set rem_bt[i] = 0
If done == true then,
Break
Step 3->In function int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int quantum)
Declare and initialize wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0
Call function waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum)
Call function turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat)
Print "Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time "
Loop For i=0 and i<n and i++
Set total_wt = total_wt + wt[i]
Set total_tat = total_tat + tat[i]
Print the value i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]
Print "Average waiting time = total_wt / n
Print "Average turnaround time =total_tat / n
Step 4-> In function int main()
Delcare and initialize processes[] = { 1, 2, 3}
Declare and initialize n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0]
Declare and initialize burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12}
Set quantum = 2
Call function findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum)示例
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate turn around time
int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int tat[]) {
// calculating turnaround time by adding
// bt[i] + wt[i]
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i];
return 1;
}
// Function to find the waiting time for all
// processes
int waitingtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int quantum) {
// Make a copy of burst times bt[] to store remaining
// burst times.
int rem_bt[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
rem_bt[i] = bt[i];
int t = 0; // Current time
// Keep traversing processes in round robin manner
// until all of them are not done.
while (1) {
bool done = true;
// Traverse all processes one by one repeatedly
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
// If burst time of a process is greater than 0
// then only need to process further
if (rem_bt[i] > 0) {
done = false; // There is a pending process
if (rem_bt[i] > quantum) {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t += quantum;
// Decrease the burst_time of current process
// by quantum
rem_bt[i] -= quantum;
}
// If burst time is smaller than or equal to
// quantum. Last cycle for this process
else {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t = t + rem_bt[i];
// Waiting time is current time minus time
// used by this process
wt[i] = t - bt[i];
// As the process gets fully executed
// make its remaining burst time = 0
rem_bt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// If all processes are done
if (done == true)
break;
}
return 1;
}
// Function to calculate average time
int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[],
int quantum) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all processes
waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum);
// Function to find turn around time for all processes
turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat);
// Display processes along with all details
printf("Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time
");
// Calculate total waiting time and total turn
// around time
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
printf("\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d
",i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]);
}
printf("Average waiting time = %f", (float)total_wt / (float)n);
printf("
Average turnaround time = %f
", (float)total_tat / (float)n);
return 1;
}
// main function
int main() {
// process id's
int processes[] = { 1, 2, 3};
int n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0];
// Burst time of all processes
int burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12};
// Time quantum
int quantum = 2;
findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum);
return 0;
}輸出


廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP