C++ 最短作業優先(SJF)排程(搶佔式)程式
給定程序、每個程序的突發時間和一個時間片限制;任務是使用最短作業優先搶佔式方法找到並列印等待時間、週轉時間及其各自的平均時間。
什麼是最短作業優先排程?
最短作業優先排程是一種作業或程序排程演算法,它遵循非搶佔式排程規則。在這種排程中,排程程式從等待佇列中選擇完成時間最短的程序,並將 CPU 分配給該作業或程序。最短作業優先比先到先服務演算法更受歡迎,因為它更最佳化,因為它減少了平均等待時間,從而提高了吞吐量。
SJF 演算法可以是搶佔式的,也可以是非搶佔式的。搶佔式排程也稱為**最短剩餘時間優先**排程。在搶佔式方法中,當已經有正在執行的程序時,新的程序就會出現。如果新到達程序的突發時間小於正在執行程序的突發時間,則排程程式將搶佔具有較短突發時間的程序的執行。
什麼是週轉時間、等待時間和完成時間?
- **完成時間**是程序完成執行所需的時間。
**週轉時間**是程序提交到完成之間的時間間隔。
週轉時間 = 程序完成時間 - 程序提交時間
**等待時間**是週轉時間和突發時間之間的差值。
等待時間 = 週轉時間 - 突發時間
示例
我們給出了程序 P1、P2、P3、P4 和 P5,以及它們相應的突發時間如下所示
| 程序 | 突發時間 | 到達時間 |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 4 | 0 |
| P2 | 2 | 1 |
| P3 | 8 | 2 |
| P4 | 1 | 3 |
| P5 | 9 | 4 |
由於 P1 的到達時間為 0,因此它將首先執行,直到另一個程序到達。當在 1 時,程序 P2 進入,並且 P2 的突發時間小於 P1 的突發時間,因此排程程式將把 CPU 分配給程序 P2,依此類推。
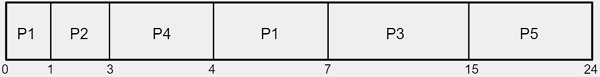
平均等待時間是根據甘特圖計算的。P1 必須等待 (0+4)4,P2 必須等待 1,P3 必須等待 7,P4 必須等待 3,P5 必須等待 15。因此,它們的平均等待時間將為 -
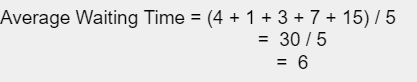
演算法
Start
Step 1-> Declare a struct Process
Declare pid, bt, art
Step 2-> In function findTurnAroundTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[], int tat[])
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set tat[i] = proc[i].bt + wt[i]
Step 3-> In function findWaitingTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[])
Declare rt[n]
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set rt[i] = proc[i].bt
Set complete = 0, t = 0, minm = INT_MAX
Set shortest = 0, finish_time
Set bool check = false
Loop While (complete != n)
Loop For j = 0 and j < n and j++
If (proc[j].art <= t) && (rt[j] < minm) && rt[j] > 0 then,
Set minm = rt[j]
Set shortest = j
Set check = true
If check == false then,
Increment t by 1
Continue
Decrement the value of rt[shortest] by 1
Set minm = rt[shortest]
If minm == 0 then,
Set minm = INT_MAX
If rt[shortest] == 0 then,
Increment complete by 1
Set check = false
Set finish_time = t + 1
Set wt[shortest] = finish_time - proc[shortest].bt -proc[shortest].art
If wt[shortest] < 0
Set wt[shortest] = 0
Increment t by 1
Step 4-> In function findavgTime(Process proc[], int n)
Declare and set wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0
Call findWaitingTime(proc, n, wt)
Call findTurnAroundTime(proc, n, wt, tat)
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set total_wt = total_wt + wt[i]
Set total_tat = total_tat + tat[i]
Print proc[i].pid, proc[i].bt, wt[i], tat[i]
Print Average waiting time i.e., total_wt / n
Print Average turn around time i.e., total_tat / n
Step 5-> In function int main()
Declare and set Process proc[] = { { 1, 5, 1 }, { 2, 3, 1 }, { 3, 6, 2 }, { 4, 5, 3 } }
Set n = sizeof(proc) / sizeof(proc[0])
Call findavgTime(proc, n)
Stop示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//structure for every process
struct Process {
int pid; // Process ID
int bt; // Burst Time
int art; // Arrival Time
};
void findTurnAroundTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[], int tat[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tat[i] = proc[i].bt + wt[i];
}
//waiting time of all process
void findWaitingTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[]) {
int rt[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
rt[i] = proc[i].bt;
int complete = 0, t = 0, minm = INT_MAX;
int shortest = 0, finish_time;
bool check = false;
while (complete != n) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if ((proc[j].art <= t) && (rt[j] < minm) && rt[j] > 0) {
minm = rt[j];
shortest = j;
check = true;
}
}
if (check == false) {
t++;
continue;
}
// decrementing the remaining time
rt[shortest]--;
minm = rt[shortest];
if (minm == 0)
minm = INT_MAX;
// If a process gets completely
// executed
if (rt[shortest] == 0) {
complete++;
check = false;
finish_time = t + 1;
// Calculate waiting time
wt[shortest] = finish_time -
proc[shortest].bt -
proc[shortest].art;
if (wt[shortest] < 0)
wt[shortest] = 0;
}
// Increment time
t++;
}
}
// Function to calculate average time
void findavgTime(Process proc[], int n) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0,
total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all
// processes
findWaitingTime(proc, n, wt);
// Function to find turn around time for
// all processes
findTurnAroundTime(proc, n, wt, tat);
cout << "Processes " << " Burst time " << " Waiting time " << " Turn around time\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
cout << " " << proc[i].pid << "\t\t" << proc[i].bt << "\t\t " << wt[i] << "\t\t " << tat[i] << endl;
}
cout << "\nAverage waiting time = " << (float)total_wt / (float)n; cout << "\nAverage turn around time = " << (float)total_tat / (float)n;
}
// main function
int main() {
Process proc[] = { { 1, 5, 1 }, { 2, 3, 1 }, { 3, 6, 2 }, { 4, 5, 3 } };
int n = sizeof(proc) / sizeof(proc[0]);
findavgTime(proc, n);
return 0;
}輸出
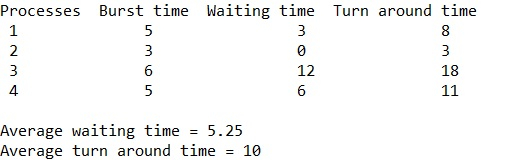

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP