Python Tkinter 中的函式繫結
在 Python 中,tkinter 是一個 GUI 庫,可用於各種 GUI 程式設計。此類應用程式對於構建桌面應用程式非常有用。在本文中,我們將瞭解 GUI 程式設計的一個方面,稱為“函式繫結”。這與將事件繫結到函式和方法有關,以便當事件發生時就會執行特定函式。
繫結鍵盤事件
在以下示例中,我們將鍵盤上的任意按鍵與其被執行的函式相關聯。Tkinter GUI 視窗開啟後,我們可以按鍵盤上的任意按鍵並收到一條訊息,表明該鍵盤已被按下。
示例
from tkinter import *
# Press a buton in keyboard
def PressAnyKey(label):
value = label.char
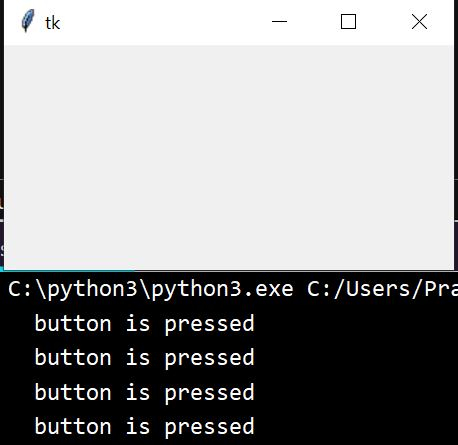
print(value, ' A button is pressed')
base = Tk()
base.geometry('300x150')
base.bind('<Key>', lambda i : PressAnyKey(i))
mainloop()
輸出
執行以上程式碼,會產生如下結果 −
繫結滑鼠單擊事件
在以下示例中,我們將瞭解如何將 Tkinter 視窗上的滑鼠單擊事件繫結到一個函式呼叫上。在以下示例中,我們將呼叫這些事件以顯示左鍵雙擊、右鍵單擊並滾動鍵單擊在 Tkinter 畫布上被單擊的位置,該畫布上是上面按鈕單擊的位置。
示例
from tkinter import *
from tkinter.ttk import *
# creates tkinter window or root window
base = Tk()
base.geometry('300x150')
# Press the scroll button in the mouse then function will be called
def scroll(label):
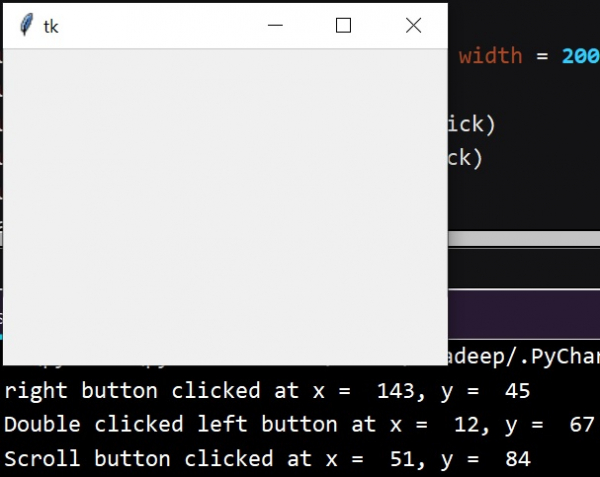
print('Scroll button clicked at x = % d, y = % d'%(label.x, label.y))
# Press the right button in the mouse then function will be called
def right_click(label):
print('right button clicked at x = % d, y = % d'%(label.x, label.y))
# Press the left button twice in the mouse then function will be called
def left_click(label):
print('Double clicked left button at x = % d, y = % d'%(label.x, label.y))
Function = Frame(base, height = 100, width = 200)
Function.bind('<Button-2>', scroll)
Function.bind('<Button-3>', right_click)
Function.bind('<Double 1>', left_click)
Function.pack()
mainloop()輸出
執行以上程式碼,會產生如下結果 −

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP