C++中的Bellman-Ford演算法?
Bellman-Ford演算法是一種動態規劃演算法,用於查詢從作為起始頂點的某個頂點計算的任何頂點的最短路徑。該演算法採用迭代方法,並不斷嘗試查詢最短路徑。Bellman-Ford演算法應用於加權圖。
該演算法由Alphonso Shimbel於1955年提出。由於Richard Bellman和Lester Ford在1956年和1958年對演算法進行了修改,因此該演算法被命名為**Bellman-Ford演算法**。Eward F. Moore也在1957年對該演算法進行了修改,這使得該演算法也被稱為**Bellman-Ford-Moore演算法**。
該演算法的優勢在於它可以處理具有負權邊的圖。儘管該演算法比Dijkstra演算法慢,但它能夠處理更通用的圖型別,因此更強大。
演算法
Input : weighted graph and starting vertex Output : shortest distance between all vertices from the src. For negative weight cycle, the same will be returned as the weight cannot be calculated.
演算法
Step 1 : This is the initialisation step, an array is created that stores the distance of all vertices from the initial vertex. The array say dist[] of size equal to the number of vertices in the graph. Step 2 : Calculate the shortest distance of vertex. Loop through step 3 for n-1 number of times ( n is the number of vertices of graph). Step 3 : Follow following steps for each edge i-j Step 3.1 : If dist[v] > dist[u] + weight[uv]. Then, dist[v] = dist[u] + weight[uv]. Step 4 : Check and flag if there is any negative cycle. If step 3.1 executes then there is a negative cycle.
負環:如果存在一條路徑比常規邊遍歷更短,則存在負環。
示例
讓我們透過解決一些與圖相關的難題來了解更多關於該演算法的資訊。
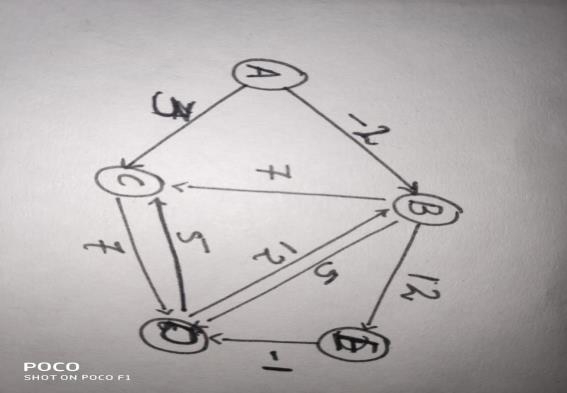
您可以看到圖的所有頂點和邊以及它們關聯的權重。
讓我們使用Bellman-Ford演算法查詢**頂點A和頂點E**之間的最短距離。
將源頂點(A)設定為零0,並將其餘距離設定為無窮大∞。
A B C D E 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞
檢查邊**A-B**然後**A-C**的權重,
對於A-B,我們只有一條路徑,但對於A-C,我們有兩條可以遍歷的路徑,我們將檢查哪一條最短。
A B C D E 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 0 -2 ∞ ∞ ∞ - for (A-B) 0 -2 3 ∞ ∞ - for (A-C)
對於接下來的頂點,我們將計算初始頂點的最短距離。
A B C D E 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 0 -2 ∞ ∞ ∞ 0 -2 3 3 10
因此,使用該演算法的最短距離是10。遍歷路徑**A-B-E**。使用此方法,我們還發現存在負環。
示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
};
struct Graph {
int V, E;
struct Edge* edge;
};
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E) {
struct Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = new Edge[E];
return graph;
}
void BellmanFord(struct Graph* graph, int src) {
int V = graph->V;
int E = graph->E;
int dist[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
dist[src] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < E; j++) {
int u = graph->edge[j].src;
int v = graph->edge[j].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[j].weight;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = graph->edge[i].src;
int v = graph->edge[i].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[i].weight;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
printf("Graph contains negative weight cycle");
return;
}
}
printf("Vertex :\t\t\t ");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t", i);
printf("\nDistance From Source : ");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t",dist[i]);
return;
}
int main() {
int V = 5;
int E = 8;
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
graph->edge[0].weight = -1;
graph->edge[1].src = 0;
graph->edge[1].dest = 2;
graph->edge[1].weight = 4;
graph->edge[2].src = 1;
graph->edge[2].dest = 2;
graph->edge[2].weight = 3;
graph->edge[3].src = 1;
graph->edge[3].dest = 3;
graph->edge[3].weight = 2;
graph->edge[4].src = 1;
graph->edge[4].dest = 4;
graph->edge[4].weight = 2;
graph->edge[5].src = 3;
graph->edge[5].dest = 2;
graph->edge[5].weight = 5;
graph->edge[6].src = 3;
graph->edge[6].dest = 1;
graph->edge[6].weight = 1;
graph->edge[7].src = 4;
graph->edge[7].dest = 3;
graph->edge[7].weight = -3;
BellmanFord(graph, 0);
return 0;
}輸出
Vertex : 0 1 2 3 4 Distance From Source : 0 -1 2 -2 1

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP