克魯斯卡爾最小生成樹演算法 - C++ 中的貪心演算法
生成樹是一個連線所有頂點的連通且無向的圖子圖。一個圖中可以存在許多生成樹。每個圖上的最小生成樹(MST)的權重都等於或小於所有其他生成樹。權重被分配到生成樹的邊上,並且總權重是每個邊分配權重的總和。由於 V 是圖中頂點的數量,因此最小生成樹具有 (V - 1) 條邊,其中 V 是邊的數量。
使用克魯斯卡爾演算法尋找最小生成樹
所有邊都應按權重非降序排列。
選擇最小的邊。如果不會形成環,則包含這條邊。
重複步驟 2,直到生成樹具有 (V-1) 條邊。
在這種情況下,我們被告知要使用貪心方法。貪心選擇是選擇權重最小的邊。例如:此圖的最小生成樹為 (9-1)= 8 條邊。
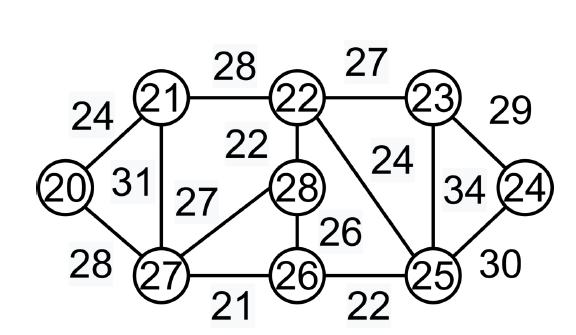
After sorting: Weight Src Dest 21 27 26 22 28 22 22 26 25 24 20 21 24 22 25 26 28 26 27 22 23 27 27 28 28 20 27 28 21 22 29 23 24 30 25 24 31 21 27 34 23 25
現在我們需要根據排序結果選擇所有邊。
邊 26-27 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環
邊 28-22 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環
邊 26-25 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環。
邊 20-21 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環
邊 22-25 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環。
邊 28-26 -> 丟棄,因為形成了環
邊 22-23 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環
邊 27-28 -> 丟棄,因為形成了環
邊 20-27 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環
邊 21-22 -> 丟棄,因為形成了環
邊 23-24 -> 包含,因為沒有形成環
由於邊的數量為 (V-1),因此演算法在此結束。
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
};
struct Graph {
int V, E;
struct Edge* edge;
};
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E){
struct Graph* graph = (struct Graph*)(malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)));
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = (struct Edge*)malloc(sizeof( struct Edge)*E);
return graph;
}
struct subset {
int parent;
int rank;
};
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i){
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent
= find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y){
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
else{
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
int myComp(const void* a, const void* b){
struct Edge* a1 = (struct Edge*)a;
struct Edge* b1 = (struct Edge*)b;
return a1->weight > b1->weight;
}
void KruskalMST(struct Graph* graph){
int V = graph->V;
struct Edge
result[V];
int e = 0;
int i = 0;
qsort(graph->edge, graph->E, sizeof(graph->edge[0]), myComp);
struct subset* subsets
= (struct subset*)malloc(V * sizeof(struct subset));
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
while (e < V - 1 && i < graph->E) {
struct Edge next_edge = graph->edge[i++];
int x = find(subsets, next_edge.src);
int y = find(subsets, next_edge.dest);
if (x != y) {
result[e++] = next_edge;
Union(subsets, x, y);
}
}
printf("Following are the edges in the constructed MST\n");
int minimumCost = 0;
for (i = 0; i < e; ++i){
printf("%d -- %d == %d\n", result[i].src,
result[i].dest, result[i].weight);
minimumCost += result[i].weight;
}
printf("Minimum Cost Spanning tree : %d",minimumCost);
return;
}
int main(){
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
30
0--------1
| \ |
26| 25\ |15
| \ |
22--------23
24 */
int V = 24;
int E = 25;
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
graph->edge[0].src = 20;
graph->edge[0].dest = 21;
graph->edge[0].weight = 30;
graph->edge[1].src = 20;
graph->edge[1].dest = 22;
graph->edge[1].weight = 26;
graph->edge[2].src = 20;
graph->edge[2].dest = 23;
graph->edge[2].weight = 25;
graph->edge[3].src = 21;
graph->edge[3].dest = 23;
graph->edge[3].weight = 35;
graph->edge[4].src = 22;
graph->edge[4].dest = 23;
graph->edge[4].weight = 24;
KruskalMST(graph);
return 0;
}輸出
Following are the edges in the constructed MST 22 -- 23 == 24 20 -- 23 == 25 20 -- 21 == 30 Minimum Cost Spanning tree : 79
結論
本教程演示瞭如何使用克魯斯卡爾最小生成樹演算法 - 貪心方法和 C++ 程式碼來解決此問題。我們也可以用 Java、Python 和其他語言編寫此程式碼。它以克魯斯卡爾的理念為模型。此程式在給定圖中找到最短的生成樹。希望本教程對您有所幫助。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP