C語言中的realloc是什麼?
C 庫記憶體分配函式 void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size) 嘗試重新調整由 ptr 指向的記憶體塊的大小,該記憶體塊之前已透過呼叫 malloc 或 calloc 分配。
記憶體分配函式
記憶體可以以兩種方式分配,如下所述:
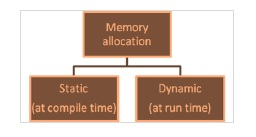
一旦在編譯時分配了記憶體,就不能在執行期間更改它。這將導致記憶體不足或記憶體浪費的問題。
解決方案是在程式執行期間根據使用者的需求動態建立記憶體。
用於動態記憶體管理的標準庫函式如下:
- malloc ( )
- calloc ( )
- realloc ( )
- free ( )
realloc ( ) 函式
它用於重新分配已分配的記憶體。
它可以減少或增加分配的記憶體。
它返回一個指向重新分配記憶體的基地址的 void 指標。
realloc() 函式的語法如下:
Free void *realloc (pointer, newsize);
示例
以下示例顯示了 realloc() 函式的使用。
int *ptr; ptr = (int * ) malloc (1000);// we can use calloc also - - - - - - - - - ptr = (int * ) realloc (ptr, 500); - - - - - - ptr = (int * ) realloc (ptr, 1500);
示例
以下是使用 realloc() 函式的 C 程式:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
int *ptr, i, num;
printf("array size is 5
");
ptr = (int*)calloc(5, sizeof(int));
if(ptr==NULL){
printf("Memory allocation failed");
exit(1); // exit the program
}
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++){
printf("enter number at %d: ", i);
scanf("%d", ptr+i);
}
printf("
Let's increase the array size to 7
");
ptr = (int*)realloc(ptr, 7 * sizeof(int));
if(ptr==NULL){
printf("Memory allocation failed");
exit(1); // exit the program
}
printf("
enter 2 more integers
");
for(i = 5; i < 7; i++){
printf("Enter element number at %d: ", i);
scanf("%d", ptr+i);
}
printf("
result array is:
");
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++){
printf("%d ", *(ptr+i) );
}
return 0;
}輸出
執行上述程式時,將產生以下結果:
array size is 5 enter number at 0: 23 enter number at 1: 12 enter number at 2: 45 enter number at 3: 67 enter number at 4: 20 Let's increase the array size to 7 enter 2 more integers Enter element number at 5: 90 Enter element number at 6: 60 result array is: 23 12 45 67 20 90 60

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C程式設計
C程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP