C語言中的calloc函式是什麼?
C庫記憶體分配函式 `void *calloc(size_t nitems, size_t size)` 分配請求的記憶體並返回指向它的指標。
malloc和calloc的區別在於,malloc不將記憶體設定為零,而calloc將分配的記憶體設定為零。
記憶體分配函式
記憶體分配方式如下所示:
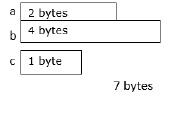
一旦在編譯時分配了記憶體,就不能在執行期間更改它。這會導致記憶體不足或浪費。
解決方案是在程式執行期間根據使用者的需求動態建立記憶體。
用於動態記憶體管理的標準庫函式如下:
- malloc()
- calloc()
- realloc()
- free()
calloc() 函式
此函式用於在執行時分配連續的記憶體塊。
它專門為陣列設計。
它返回一個void指標,該指標指向分配記憶體的基地址。
calloc()函式的語法如下:
void *calloc ( numbers of elements, size in bytes)
示例
以下示例演示了calloc()函式的使用。
int *ptr; ptr = (int * ) calloc (500,2);
這裡,將連續分配500個大小為2位元組的記憶體塊。總共分配的記憶體 = 1000位元組。
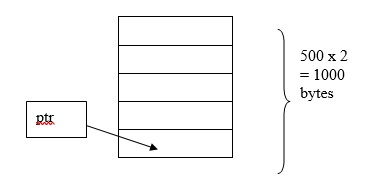
int *ptr; ptr = (int * ) calloc (n, sizeof (int));
示例程式
下面是一個C程式,它使用動態記憶體分配函式calloc計算一組元素中偶數和奇數的和。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main(){
//Declaring variables, pointers//
int i,n;
int *p;
int even=0,odd=0;
//Declaring base address p using Calloc//
p = (int * ) calloc (n, sizeof (int));
//Reading number of elements//
printf("Enter the number of elements : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
/*Printing O/p -
We have to use if statement because we have to check if memory
has been successfully allocated/reserved or not*/
if (p==NULL){
printf("Memory not available");
exit(0);
}
//Storing elements into location using for loop//
printf("The elements are :
");
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",p+i);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
if(*(p+i)%2==0){
even=even+*(p+i);
} else {
odd=odd+*(p+i);
}
}
printf("The sum of even numbers is : %d
",even);
printf("The sum of odd numbers is : %d
",odd);
}輸出
執行上述程式後,將產生以下結果:
Enter the number of elements : 4 The elements are : 12 56 23 10 The sum of even numbers is : 78 The sum of odd numbers is : 23

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C程式設計
C程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP