在具有 C++ 中任意指標的連結串列中指向下一個較大值節點
在這個問題中,我們提供了一個帶值、連結指標和任意指標的連結串列。我們的任務是使任意指標指向列表中下一個大的值。
我們舉一個例子來理解這個問題,
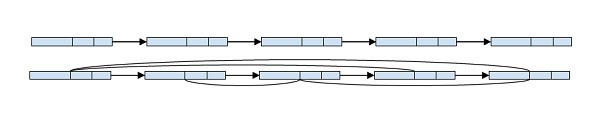
在這裡,我們可以看到 8 指向 12,12 指向 41,41 指向 54,54 指向 76,它們是連結串列中連續較大的元素。
為了解決這個問題,我們將使用歸併排序演算法對元素進行排序,並使用該排序作為任意指標的連結串列。
為此,我們將對連結串列使用歸併排序演算法,將任意指標作為排序和連結串列的主要指標,這將解決問題,即每個任意點將指向比它大的下一個節點。
示例
程式展示了我們解決方案的一個實現,
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next, *arbit;
};
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b);
void FrontBackSplit(Node* source, Node** frontRef, Node** backRef);
void MergeSort(Node** headRef) {
Node* head = *headRef;
Node* a, *b;
if ((head == NULL) || (head->arbit == NULL))
return;
FrontBackSplit(head, &a, &b);
MergeSort(&a);
MergeSort(&b);
*headRef = SortedMerge(a, b);
}
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b) {
Node* result = NULL;
if (a == NULL)
return (b);
else if (b == NULL)
return (a);
if (a->data <= b->data){
result = a;
result->arbit = SortedMerge(a->arbit, b);
} else {
result = b;
result->arbit = SortedMerge(a, b->arbit);
}
return (result);
}
void FrontBackSplit(Node* source, Node** frontRef, Node** backRef) {
Node* fast, *slow;
if (source == NULL || source->arbit == NULL){
*frontRef = source;
*backRef = NULL;
return;
}
slow = source, fast = source->arbit;
while (fast != NULL){
fast = fast->arbit;
if (fast != NULL){
slow = slow->arbit;
fast = fast->arbit;
}
}
*frontRef = source;
*backRef = slow->arbit;
slow->arbit = NULL;
}
void addNode(Node** head_ref, int new_data) {
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->arbit = NULL;
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
Node* populateArbitraray(Node *head) {
Node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL){
temp->arbit = temp->next;
temp = temp->next;
}
MergeSort(&head);
return head;
}
int main() {
Node* head = NULL;
addNode(&head, 45);
addNode(&head, 12);
addNode(&head, 87);
addNode(&head, 32);
Node *ahead = populateArbitraray(head);
cout << "\t\tArbitrary pointer overlaoded \n Traversing linked List\n";
cout<<"Using Next Pointer\n";
while (head!=NULL){
cout << head->data << ", ";
head = head->next;
}
printf("\nUsing Arbit Pointer\n");
while (ahead!=NULL){
cout<<ahead->data<<", ";
ahead = ahead->arbit;
}
return 0;
}輸出
Arbitrary pointer overlaoded Traversing linked List Using Next Pointer 32, 87, 12, 45, Using Arbit Pointer 12, 32, 45, 87,

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 語言程式設計
C 語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP