C++中將資訊傳遞到樹中所有節點所需的最小迭代次數
給定一個具有'n'個節點的樹形資料結構。給定的樹將有一個根節點和各自的子節點,子節點數量可以是任意數量,並且進一步的子節點可以有任意數量的子節點。任務是找到樹的根節點將資訊傳遞到樹中所有節點所需的最小迭代次數。一次,一個節點可以將資訊傳遞給它的一個子節點,然後它的一個子節點可以將資訊傳遞給它的一個子節點,同時根節點可以將資訊傳遞給另一個子節點。
讓我們看看這個的各種輸入輸出場景 -
輸入 -
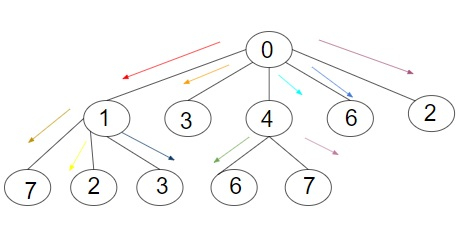
輸出 -將資訊傳遞到樹中所有節點所需的最小迭代次數為:5
解釋 -給定一個樹,共有11個節點,包括根節點和其他所有節點。給定樹的根節點是0,它將首先將資料傳遞給節點1(因為它有很多子節點,然後是其他節點),然後根節點將資料傳遞給節點4,然後傳遞給3,然後傳遞給6,最後傳遞給2。因此,總共需要的迭代次數為5。
輸入 -
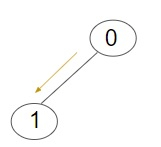
輸出 -將資訊傳遞到樹中所有節點所需的最小迭代次數為:1
解釋 -給定一個樹,共有2個節點,包括根節點和其他所有節點。由於給定樹中根節點只有一個子節點,因此所需的最小迭代次數為1。
下面程式中使用的方法如下:
建立一個類來構建樹,並新增節點作為其資料成員,建立一個列表指標作為List_children,並宣告一個私有方法void Iteration(int vertices, int arr[])。宣告一個引數化建構函式Tree(int nodes)、void insert_node(int a, int b)、int Min_Iteration()和靜態int check(const void *a_1, const void *b_1)。
呼叫外部引數化建構函式Tree::Tree(int nodes)
將this->nodes設定為nodes。
將List_children設定為new list[nodes]
呼叫類方法void Tree::insert_node(int a, int b)
將List_children[a]設定為push_back(b)
呼叫類方法void Tree::Iteration(int vertices, int arr[])
將arr[vertices]設定為List_children[vertices].size()
將*ptr設定為new int[arr[vertices]]
將temp設定為0,temp_2設定為0
宣告一個迭代器list::iterator it
從it到List_children[vertices].begin()開始迴圈,直到it不等於List_children[vertices].end(),並預增量it。在迴圈內設定Iteration(*it, arr)並將ptr[temp++]設定為arr[*it]
呼叫qsort(ptr, arr[vertices], sizeof(int), check)進行快速排序
從temp為0開始迴圈,直到temp小於List_children[vertices].size(),並後增量temp。在迴圈內,將temp_2設定為ptr[temp] + temp + 1,並將arr[vertices]設定為max(arr[vertices], temp_2),並刪除[] ptr
呼叫類方法int Tree::Min_Iteration()
宣告一個指標int *ptr = new int[nodes]
宣告一個變數int temp = -1
從i為0開始迴圈,直到i < nodes並i++。在迴圈內,將ptr[i]設定為0
呼叫Iteration(0, ptr)並將temp設定為ptr[0],並刪除[] ptr
返回temp
呼叫類方法int Tree::check(const void * a_1, const void * b_1)
宣告一個變數int result為(*(int*)b_1 - *(int*)a_1)
返回result
在main()函式中
使用引數化建構函式建立一個樹物件。
然後使用樹類的物件呼叫insert_node()方法將節點資料插入到樹中
呼叫Min_Iteration()方法計算將資訊傳遞到樹中所有節點所需的最小迭代次數
示例
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
int nodes;
list<int> *List_children;
void Iteration(int vertices, int arr[]);
public:
//constructor of a class
Tree(int nodes);
//method to insert a node in a tree
void insert_node(int a, int b);
//method to calculate the minimum iterations
int Min_Iteration();
static int check(const void *a_1, const void *b_1);
};
Tree::Tree(int nodes)
{
this->nodes = nodes;
List_children = new list<int>[nodes];
}
void Tree::insert_node(int a, int b)
{
List_children[a].push_back(b);
}
void Tree::Iteration(int vertices, int arr[])
{
arr[vertices] = List_children[vertices].size();
int *ptr = new int[arr[vertices]];
int temp = 0;
int temp_2 = 0;
list<int>::iterator it;
for(it = List_children[vertices].begin(); it!= List_children[vertices].end(); ++it)
{
Iteration(*it, arr);
ptr[temp++] = arr[*it];
}
qsort(ptr, arr[vertices], sizeof(int), check);
for(temp = 0; temp < List_children[vertices].size(); temp++)
{
temp_2 = ptr[temp] + temp + 1;
arr[vertices] = max(arr[vertices], temp_2);
}
delete[] ptr;
}
int Tree::Min_Iteration()
{
int *ptr = new int[nodes];
int temp = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++)
{
ptr[i] = 0;
}
Iteration(0, ptr);
temp = ptr[0];
delete[] ptr;
return temp;
}
int Tree::check(const void * a_1, const void * b_1)
{
}
int main()
{
Tree T_1(8);
T_1.insert_node(0, 1);
T_1.insert_node(0, 3);
T_1.insert_node(0, 4);
T_1.insert_node(0, 6);
T_1.insert_node(0, 2);
T_1.insert_node(1, 7);
T_1.insert_node(1, 2);
T_1.insert_node(1, 3);
T_1.insert_node(4, 6);
T_1.insert_node(4, 7);
cout<<"Minimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are:"<<T_1.Min_Iteration();
Tree T_2(2);
T_2.insert_node(0, 1);
cout<<"\nMinimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are:" <<T_1.Min_Iteration();
return 0;
}輸出
如果執行上述程式碼,它將生成以下輸出
Minimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are: 8 Minimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are: 8


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP