Lamport麵包店演算法
Lamport麵包店演算法是一種同步方法,用於解決平行計算系統中的臨界區問題。臨界區問題發生在多個程序同時需要訪問共享資源,但同一時間只有一個程序可以訪問的情況。挑戰在於確保每個程序以互斥的方式訪問資源,以避免衝突並保證系統的正確性。
Lamport麵包店演算法的虛擬碼
以下是Lamport麵包店演算法的虛擬碼:
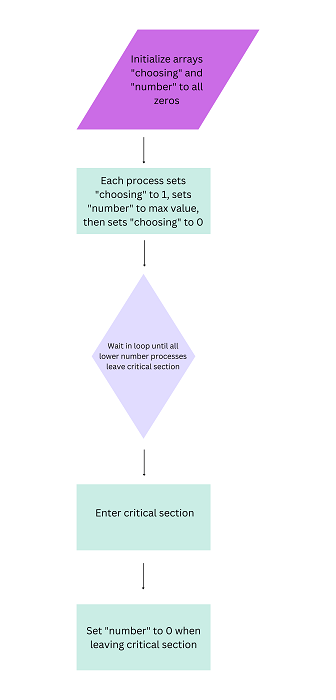
初始化一個大小為N的陣列choosing,其中N是程序的總數,所有元素都設定為0。
初始化一個大小為N的陣列number,所有元素都設定為0。
當每個程序i想要進入臨界區時,執行以下程式碼:
設定choosing[i] = 1
設定number[i] = max(number[0], number[1], ..., number[N-1]) + 1
設定choosing[i] = 0
對於其他每個程序j,重複執行以下操作,直到(number[j] == 0) 或 (number[i], i) < (number[j], j):等待
進入臨界區
當每個程序i離開臨界區時,執行以下程式碼:
設定number[i] = 0
Lamport麵包店演算法的程式碼
以下程式碼演示了Lamport麵包店演算法的實際應用。本例中,我們將使用C++作為實現語言。
#include <iostream>
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#define N 5
// total number of processes
using namespace std;
atomic<bool> entering[N] = {false};
// to keep track of which process is currently trying to enter critical section
atomic<int> number[N] = {0};
// to hold the ticket number for each process
void process(int i) {
while (true) {
// Step 1: Get ticket number
entering[i] = true;
int max_number = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (number[j] > max_number) {
max_number = number[j];
}
}
number[i] = max_number + 1;
entering[i] = false;
// Step 2: Wait until it is this process's turn to enter the critical section
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
while (entering[j]) {}
// wait until process j has finished choosing its ticket number
while ((number[j] != 0) && ((number[j] < number[i]) || ((number[j] == number[i]) && j < i))) {}
// busy wait until it is this process's turn to enter the critical section
}
// Step 3: Enter the critical section
cout << "Process " << i << " enters the critical section." << endl;
// perform critical section operations here
// Step 4: Exit the critical section
number[i] = 0;
cout << "Process " << i << " exits the critical section." << endl;
// perform remainder section operations here
}
}
int main() {
// create threads for each process
thread t[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
t[i] = thread(process, i);
}
// join threads
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
t[i].join();
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Process 0 enters the critical section. Process 0 exits the critical section. Process 1 enters the critical section. Process 1 exits the critical section. Process 2 enters the critical section. Process 2 exits the critical section. Process 3 enters the critical section. Process 3 exits the critical section. Process 0 enters the critical section. Process 0 exits the critical section. Process 1 enters the critical section. Process 1 exits the critical section. Process 4 enters the critical section. Process 4Process exits the critical section.2 .............
Lamport麵包店演算法的優點
以下是Lamport麵包店演算法的優點:
透過為請求訪問共享資源的程序或執行緒分配唯一的號碼,確保公平性。
根據分配的號碼分配號碼,防止飢餓。
基於號碼的策略簡單易懂,易於實現。
高效,不需要複雜的資料結構或程序間通訊。
提供互斥,無需專用硬體或硬體支援。
廣泛適用且靈活,可應用於各種場景,以確保併發計算中的公平性和互斥。
對於從事分散式或並行系統工作的軟體工程師來說,這是一個有用的工具。
Lamport麵包店演算法的缺點
忙等待 - 該演算法需要忙等待,這可能會導致低效率和高CPU利用率,尤其是在許多程序或執行緒競爭訪問同一共享資源時。
飢餓 - 雖然該演算法保證公平性,但沒有防止飢餓的保護措施。一個程序或執行緒有時可能會被無限期地延遲,從而無法獲得號碼並訪問資源。
開銷 - 該演算法需要額外的記憶體和處理時間來確定號碼序列,因為它需要為每個程序或執行緒儲存狀態資訊。
複雜性 - 該演算法的實現可能很複雜,因為它需要仔細處理競爭條件和死鎖,並且可能需要使用諸如互斥鎖或訊號量的同步機制。
結論
Lamport麵包店演算法是一種互斥演算法,它確保多個程序或執行緒可以訪問共享資源而不會相互干擾。它是一個簡單的演算法,可以防止飢餓並確保公平性。
該演算法透過為每個請求訪問資源的程序或執行緒分配號碼,然後比較這些號碼的值來確定它們被服務的順序。資源首先被分配給號碼最小的程序。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP