C++ 中的線索二叉樹的中序遍歷
這裡我們將瞭解線索二叉樹資料結構。我們知道二叉樹節點最多有兩個子節點。但如果它們只有一個子節點或沒有子節點,那麼在連結串列表示中,連結部分將保持為 null。使用線索二叉樹表示時,我們可以透過建立一些執行緒來重用這些空連結。
如果某個節點有一些空閒的左或右子節點區域,那將用作執行緒。線索二叉樹有兩種型別:單線索樹或全線索二叉樹。
對於全線索二叉樹,每個節點都有五個欄位。三個欄位與正常二叉樹節點類似,另外兩個欄位用於儲存布林值,以表示該側的連結是實際連結還是執行緒。
| 左執行緒標誌 | 左連結 | 資料 | 右連結 | 右執行緒標誌 |
這是全線索二叉樹
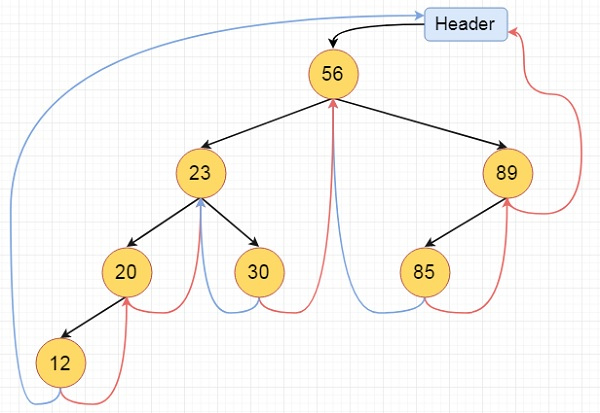
演算法
inorder(): Begin temp := root repeat infinitely, do p := temp temp = right of temp if right flag of p is false, then while left flag of temp is not null, do temp := left of temp done end if if temp and root are same, then break end if print key of temp done End
示例
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_VALUE 65536
using namespace std;
class N { //node declaration
public:
int k;
N *l, *r;
bool leftTh, rightTh;
};
class ThreadedBinaryTree {
private:
N *root;
public:
ThreadedBinaryTree() { //constructor to initialize the variables
root= new N();
root->r= root->l= root;
root->leftTh = true;
root->k = MAX_VALUE;
}
void insert(int key) {
N *p = root;
for (;;) {
if (p->k< key) { //move to right thread
if (p->rightTh)
break;
p = p->r;
}
else if (p->k > key) { // move to left thread
if (p->leftTh)
break;
p = p->l;
}
else {
return;
}
}
N *temp = new N();
temp->k = key;
temp->rightTh= temp->leftTh= true;
if (p->k < key) {
temp->r = p->r;
temp->l= p;
p->r = temp;
p->rightTh= false;
}
else {
temp->r = p;
temp->l = p->l;
p->l = temp;
p->leftTh = false;
}
}
void inorder() { //print the tree
N *temp = root, *p;
for (;;) {
p = temp;
temp = temp->r;
if (!p->rightTh) {
while (!temp->leftTh) {
temp = temp->l;
}
}
if (temp == root)
break;
cout<<temp->k<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
};
int main() {
ThreadedBinaryTree tbt;
cout<<"Threaded Binary Tree\n";
tbt.insert(56);
tbt.insert(23);
tbt.insert(89);
tbt.insert(85);
tbt.insert(20);
tbt.insert(30);
tbt.insert(12);
tbt.inorder();
cout<<"\n";
}輸出
Threaded Binary Tree 12 20 23 30 56 85 89

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP