如何在 C 語言中使用指標來乘以兩個矩陣?
指標是一個儲存另一個變數地址的變數。
指標的特性
- 指標節省記憶體空間。
- 由於可以直接訪問記憶體位置,因此指標的執行時間更快。
- 藉助指標,可以有效地訪問記憶體,即動態分配和釋放記憶體。
- 指標用於資料結構。
指標的宣告、初始化和訪問
考慮以下語句:
int qty = 179;
在記憶體中,變數可以表示如下:
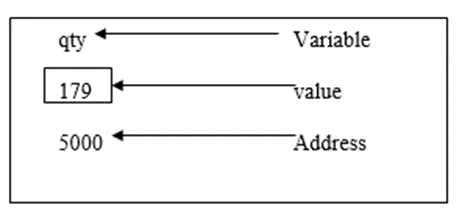
宣告
宣告指標可以如下所示:
Int *p;
這意味著“p”是一個指標變數,它儲存另一個整型變數的地址。
初始化
地址運算子 (&) 用於初始化指標變數。
例如:
int qty = 175; int *p; p= &qty;
透過指標訪問變數
要訪問變數的值,使用間接運算子 (*)。
示例
以下是用指標乘以兩個矩陣的 C 程式:
#include <stdio.h>
#define ROW 3
#define COL 3
/* Function declarations */
void matrixInput(int mat[][COL]);
void matrixPrint(int mat[][COL]);
void matrixMultiply(int mat1[][COL], int mat2[][COL], int res[][COL]);
int main() {
int mat1[ROW][COL];
int mat2[ROW][COL];
int product[ROW][COL];
printf("Enter elements in first matrix of size %dx%d
", ROW, COL);
matrixInput(mat1);
printf("Enter elements in second matrix of size %dx%d
", ROW, COL);
matrixInput(mat2);
matrixMultiply(mat1, mat2, product);
printf("Product of both matrices is :
");
matrixPrint(product);
return 0;
}
void matrixInput(int mat[][COL]) {
int row, col;
for (row = 0; row < ROW; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < COL; col++) {
scanf("%d", (*(mat + row) + col));
}
}
}
void matrixPrint(int mat[][COL]) {
int row, col;
for (row = 0; row < ROW; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < COL; col++) {
printf("%d ", *(*(mat + row) + col));
}
printf("
");
}
}
void matrixMultiply(int mat1[][COL], int mat2[][COL], int res[][COL]) {
int row, col, i;
int sum;
for (row = 0; row < ROW; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < COL; col++) {
sum = 0;
for (i = 0; i < COL; i++) {
sum += (*(*(mat1 + row) + i)) * (*(*(mat2 + i) + col));
}
*(*(res + row) + col) = sum;
}
}
}輸出
執行上述程式後,將產生以下輸出:
Enter elements in first matrix of size 3x3 2 3 1 2 5 6 2 6 8 Enter elements in second matrix of size 3x3 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Product of both matrices is : 13 19 21 42 55 64 54 70 82

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP