如何使用JDBC將檔案插入/儲存到MySQL資料庫中?
通常,檔案內容儲存在MySQL資料庫中的**Clob** (TINYTEXT, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXT) 資料型別下。
JDBC支援Clob資料型別,用於將檔案內容儲存到資料庫中的表中。
**PreparedStatement** 介面的**setCharacterStream()** 方法接受一個表示引數索引的整數和一個Reader物件作為引數。
並將給定Reader物件(檔案)的內容設定為指定索引中引數(佔位符)的值。
當您需要傳送非常大的文字值時,可以使用此方法。
使用JDBC儲存文字檔案
如果您需要使用JDBC程式將檔案儲存到資料庫中,請建立具有Clob (TINYTEXT, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXT) 資料型別的表,如下所示:
CREATE TABLE Articles(Name VARCHAR(255), Article LONGTEXT);
現在,使用JDBC連線到資料庫並準備一個**PreparedStatement** 來將值插入到上面建立的表中。
String query = "INSERT INTO Tutorial(Name, Article) VALUES (?,?)";PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(query);
使用PreparedStatement介面的setter方法設定佔位符的值,對於Clob資料型別,使用**setCharacterStream()**方法設定值。
示例
以下示例演示如何使用JDBC程式將檔案插入到MySQL資料庫中。這裡我們建立了一個具有Clob資料型別的表,並將值插入其中。
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class InsertingFileToDatabase {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
//Registering the Driver
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
//Getting the connection
String mysqlUrl = "jdbc:mysql:///sampleDB";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(mysqlUrl, "root", "password");
System.out.println("Connection established......");
//Inserting values
String query = "INSERT INTO Articles(Name, Article) VALUES (?, ?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setString(1, "article1");
FileReader reader = new FileReader("E:\data\article1.txt");
pstmt.setCharacterStream(2, reader);
pstmt.execute();
pstmt.setString(1, "article2");
reader = new FileReader("E:\data\article2.txt");
pstmt.setCharacterStream(2, reader);
pstmt.execute();
pstmt.setString(1, "article3");
reader = new FileReader("E:\data\article3.txt");
pstmt.setCharacterStream(2, reader);
pstmt.execute();
System.out.println("Data inserted......");
}
}輸出
Connection established...... Data inserted......
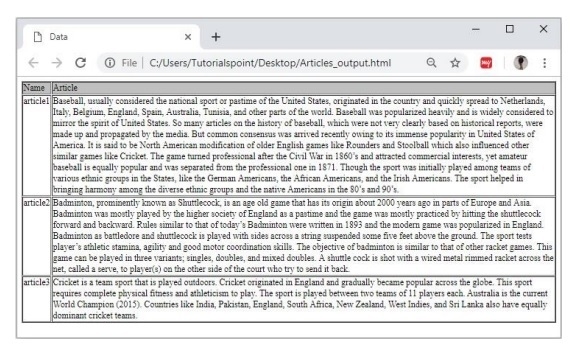
使用MySQL Workbench,您可以將表的內容匯出到各種檔案,例如html檔案、.csv檔案、文字檔案等。如果您在將資料插入到HTML檔案後匯出表的內容,其輸出將如下所示:

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP