用合適的 C 語言示例解釋字串庫函式
字串庫函式
在 string.h 庫 中提供了用於處理字串的預定義函式。它們是:
strlen () 函式
它返回字串中的字元數。
語法
int strlen (string name)
示例
#include <string.h> main (){ char a[30] = “Hello”; int l; l = strlen (a); printf (“length of the string = %d”, l); getch (); }
輸出
length of the string = 5
strcpy () 函式
- 它用於將源字串複製到目標字串。
- 目標字串的長度 >= 源字串。
語法
strcpy (Destination string, Source String);
例如,
1) char a[50]; strcpy (“Hello”,a); o/p: error 2) char a[50]; strcpy ( a,”hello”); o/p: a= “Hello”
示例
#include <string.h> main (){ char a[50], b[50]; printf ("enter a source string"); scanf("%s", a); printf("enter destination string"); scanf("%s",b); strcpy ( b,a); printf ("copied string = %s",b); getch (); }
輸出
Enter a source string : Hello Copied string = Hello
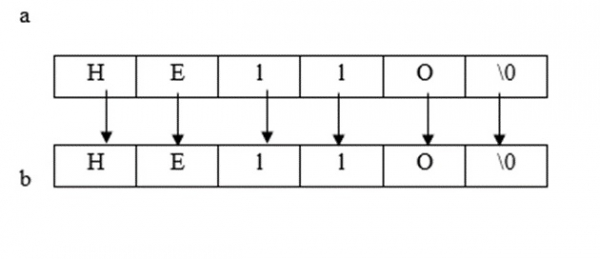
strncpy () 函式
它將源字串的 'n' 個字元複製到目標字串。
目標字串的長度必須 >= 源字串。
語法
strncpy (Destination string, Source String, n);
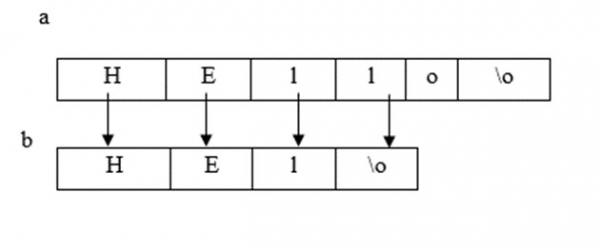
示例
#include<string.h> main (){ char a[50], b[50]; printf ("enter a string"); gets (a); gets(b); strncpy (b,a,3);// copy first 3 char from a string b[3] = '\0'; printf ("copied string = %s",b); getch (); }
輸出
Enter a string : Hello Copied string = Hel It is also used for extracting substrings;
strcat () 函式
- 它組合兩個字串。
- 目標字串的長度必須 > 源字串。
語法
strcat (Destination String, Source string);
示例
#include <string.h> main(){ char a[50] = "Hello"; char b[20] = "Good Morning"; clrscr (); strcat (a,b); printf("concatenated string = %s", a); getch (); }
輸出
Concatenated string = Hello Good Morning
strncat () 函式
此函式用於將一個字串的 n 個字元連線到另一個字串。
目標字串的長度必須大於源字串
結果連線後的字串將儲存在目標字串中。
語法
strncat (Destination String, Source string,n);
示例
#include <string.h> main (){ char a [30] = "Hello"; char b [20] = "Good Morning"; clrscr (); strncat (a,b,4); a [9] = '\0'; printf("concatenated string = %s", a); getch (); }
輸出
Concatenated string = Hello Good.
strcmp() 函式(字串比較)
此函式比較兩個字串。
它返回兩個字串中前兩個不匹配字元的 ASCII 差值。
語法
int strcmp (string1, string2); //If the difference is equal to zero, then string1 = string2 //If the difference is positive, then string1 > string2 //If the difference is negative, then string1 < string2

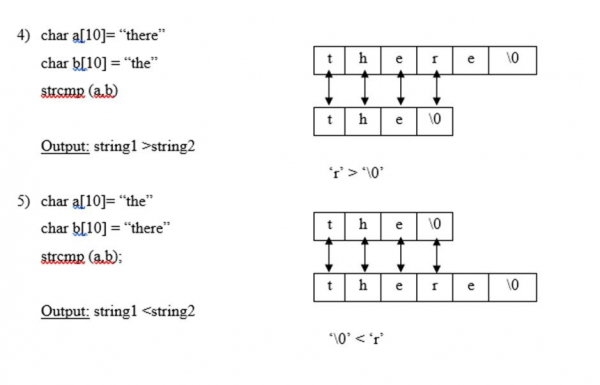
示例
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> int main (){ char a[50], b [50]; int d; printf ("Enter 2 strings:"); scanf ("%s %s", a,b); d = strcmp(a,b); if (d==0){ printf("%s is (alphabetically) equal to %s", a,b); }else if (d>0){ printf("%s is (alphabetically) greater than %s",a,b); }else if (d<0){ printf("%s is (alphabetically) less than %s", a,b); } }
輸出
Enter 2 strings:apple ball apple is (alphabetically) less than ball
strncmp () 函式
此函式用於比較兩個字串的前 'n' 個字元。
語法
strncmp ( string1, string2,2)
例如,char a[10] = “the”;
char b[10] = “there”
strncmp (a,b,4);
輸出 - 兩個字串相等
strrev() 函式
- 該函式用於反轉字串。
- 反轉後的字串將儲存在同一個字串中。
語法
strrev (string)
示例
#include<stdio.h> main (){ char a[50] ; clrscr(); printf ("enter a string"); gets (a); strrev (a); printf("reversed string = %s",a) getch (); }
輸出
enter a string Hello reversed string = olleH
strstr() 函式
它用於搜尋子字串是否在主字串中。
它返回 s1 中 s2 第一次出現的指標。
語法
strstr(mainsring,substring);
示例
#include<stdio.h> void main(){ char a[30],b[30]; char *found; printf("Enter a string:\t"); gets(a); printf("Enter the string to be searched for:\t"); gets(b); found=strstr(a,b); if(found) printf("%s is found in %s in %d position",b,a,found-a); else printf("-1 since the string is not found"); getch(); }
輸出
Enter a string: how are you Enter the string to be searched for: you you is found in 8 position

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統
關係資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP