用 C 語言解釋算術指標操作?
指標是一種變數,它儲存著另一個變數的地址。
指標宣告、初始化以及獲取
考慮以下語句 −
int qty = 179;

宣告指標
int *p;
‘p’是一個指標變數,它儲存著另一個整型變數的地址。
指標初始化
地址運算子 (&) 用於初始化指標變數。
int qty = 175; int *p; p= &qty;
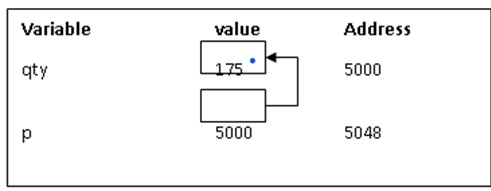
使用指標的算數運算
指標變數可以在表示式中使用。例如,如果指標變數正確宣告和初始化,那麼以下語句是有效的。
a) *p1 + *p2 b) *p1- *p2 c) *p1 * *p2 d) *p1/ *p2 Note: There must be a blank space between / and * otherwise it is treated as beginning of comment line e ) p1 + 4 f) p2 - 2 g) p1 - p2 Note: returns the no. of elements in between p1 and p2 if both of them point to same array h) p1++ i) – – p2 j) sum + = *p2 j) p1 > p2 k) p1 = = p2 l) p1 ! = p2 Note: Comparisons can be used meaningfully in handling arrays and strings
以下語句無效 −
a) p1 + p2 b) p1 * p2 c) p1 / p2 d) p1 / 3
程式
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int a,b,x,y,z;
int *p1, *p2;
a =12;
b = 4;
p1= &a;
p2 = &b;
x = *p1 * * p2 – 6;
y= 4 - *p2 / *p1+10;
printf (“Address of a = %d”, p1);
printf (“Address of b = %d”, p2);
printf (“a= %d b =%d”, a,b);
printf (“x= %d y =%d”, x,y);
}輸出
Address of a = 1234 Address of b = 5678 a = 12 b= 4 x = 42 y= 14
解釋


廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路技術
網路技術 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP