C++ 最佳頁面置換演算法程式
給定頁面數量和頁面大小;任務是找到使用最佳頁面置換演算法分配記憶體塊到頁面時命中的次數和未命中的次數。
什麼是最佳頁面置換演算法?
最佳頁面置換演算法是一種頁面置換演算法。頁面置換演算法是一種決定哪個記憶體頁面需要被替換的演算法。在最佳頁面置換中,我們替換將來短期內不會被引用的頁面,儘管它在實踐中無法實現,但它是最優的並且具有最少的未命中,並且是最優的。
讓我們透過使用一個例子並以圖解方式解釋它來理解。
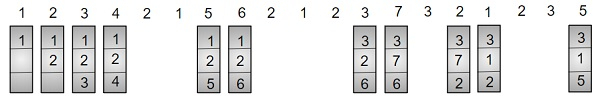
在這裡,在分配 1、2 和 3 之後,記憶體已滿,因此為了插入 4,我們將查詢從 1、2 和 3 中將來短期內不會再次引用的頁面,因此頁面 3 在將來短期內不會被引用,因此我們用新頁面 4 替換該頁面,依此類推,我們將重複這些步驟直到到達末尾。
示例
Input: page[] = { 1, 7, 8, 3, 0, 2, 0, 3, 5, 4, 0, 6, 1 }
fn=3
Output: Hits = 3
Misses = 10
Input: page[] = { 7, 0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 4, 2, 3, 0, 3, 2 }
fn = 4
Output: Hits = 7
Misses= 6我們用來解決上述問題的方法 -
- 將頁面作為陣列輸入。
- 查詢已分配的頁面是否在將來短期記憶體在,如果不存在,則用新頁面替換記憶體中的該頁面,
- 如果頁面已存在,則命中次數加 1,否則未命中次數加 1。
- 重複此操作,直到到達陣列的最後一個元素。
- 列印命中次數和未命中次數。
演算法
Start
Step 1-> In function int predict(int page[], vector<int>& fr, int pn, int index)
Declare and initialize res = -1, farthest = index
Loop For i = 0 and i < fr.size() and i++
Loop For j = index and j < pn and j++
If fr[i] == page[j] then,
If j > farthest
Set farthest = j
End If
Set res = i
break
If j == pn then,
Return i
Return (res == -1) ? 0 : res
Step 2-> In function bool search(int key, vector<int>& fr)
Loop For i = 0 and i < fr.size() and i++
If fr[i] == key then,
Return true
Return false
Step 3-> In function void opr(int page[], int pn, int fn)
Declare vector<int> fr
Set hit = 0
Loop For i = 0 and i < pn and i++
If search(page[i], fr) then,
Increment hit by 1
continue
If fr.size() < fn then,
fr.push_back(page[i])
Else
Set j = predict(page, fr, pn, i + 1)
Set fr[j] = page[i]
Print the number of hits
Print the number of misses
Step 4-> In function int main()
Declare and assign page[] = { 1, 7, 8, 3, 0, 2, 0, 3, 5, 4, 0, 6, 1 }
Set pn = sizeof(page) / sizeof(page[0])
Set fn = 3
opr(page, pn, fn)
Stop示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int predict(int page[], vector<int>& fr, int pn, int index) {
// Store the index of pages which are going
// to be used recently in future
int res = -1, farthest = index;
for (int i = 0; i < fr.size(); i++) {
int j;
for (j = index; j < pn; j++) {
if (fr[i] == page[j]) {
if (j > farthest) {
farthest = j;
res = i;
}
break;
}
}
// Return the page which are
// are never referenced in future,
if (j == pn)
return i;
}
// If all of the frames were not in future,
// return any of them, we return 0. Otherwise
// we return res.
return (res == -1) ? 0 : res;
}
bool search(int key, vector<int>& fr) {
for (int i = 0; i < fr.size(); i++)
if (fr[i] == key)
return true;
return false;
}
void opr(int page[], int pn, int fn) {
vector<int> fr;
int hit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < pn; i++) {
// Page found in a frame : HIT
if (search(page[i], fr)) {
hit++;
continue;
}
//If a page not found in a frame : MISS
// check if there is space available in frames.
if (fr.size() < fn)
fr.push_back(page[i]);
// Find the page to be replaced.
else {
int j = predict(page, fr, pn, i + 1);
fr[j] = page[i];
}
}
cout << "Hits = " << hit << endl;
cout << "Misses = " << pn - hit << endl;
}
// main Function
int main() {
int page[] = { 1, 7, 8, 3, 0, 2, 0, 3, 5, 4, 0, 6, 1 };
int pn = sizeof(page) / sizeof(page[0]);
int fn = 3;
opr(page, pn, fn);
return 0;
}輸出
Hits = 3 Misses = 10

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP