Python Tkinter 中的 after 方法
Tkinter 是一個用於製作 GUI 的 python 庫。它提供了許多內建方法來建立和控制 GUI 視窗以及用於展示資料和 GUI 事件的其他小元件。在本文中,我們將瞭解 after 方法如何在 Tkinter GUI 中使用。
語法
.after(delay, FuncName=FuncName) This method calls the function FuncName after the given delay in milisecond
顯示小元件
這裡我們製作一個框架來隨機顯示一個單詞列表。我們使用 random 庫以及 after 方法來呼叫一個函式,以一種隨機方式顯示一個給定的文字列表。
示例
import random from tkinter import * base = Tk() a = Label(base, text="After() Demo") a.pack() contrive = Frame(base, width=450, height=500) contrive.pack() words = ['Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri','Sat','Sun'] #Display words randomly one after the other. def display_weekday(): if not words: return rand = random.choice(words) character_frame = Label(contrive, text=rand) character_frame.pack() contrive.after(500,display_weekday) words.remove(rand) base.after(0, display_weekday) base.mainloop()
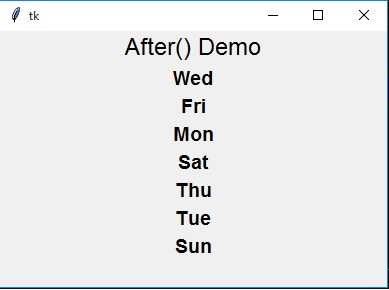
執行以上程式碼會得到以下結果
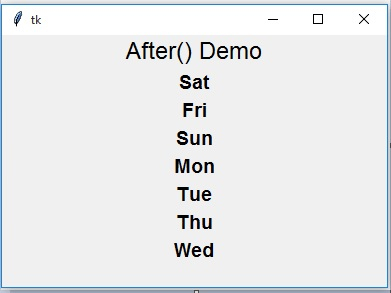
再次運行同樣的程式,會得到展示單詞不同序列的結果。
停止處理
在下一個示例中,我們將看到如何使用 after 方法作為一種延遲機制,等待一個程序執行一段時間,然後停止程序。我們還使用 destroy 方法來停止處理。
示例
from tkinter import Tk, mainloop, TOP
from tkinter.ttk import Button
from time import time
base = Tk()
stud = Button(base, text = 'After Demo()')
stud.pack(side = TOP, pady = 8)
print('processing Begins...')
begin = time()
base.after(3000, base.destroy)
mainloop()
conclusion = time()
print('process destroyed in % d seconds' % ( conclusion-begin))執行以上程式碼會得到以下結果
processing Begins... process destroyed in 3 seconds

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP