影像處理中的形態學梯度是什麼?
腐蝕和膨脹是兩個基本的形態學操作。顧名思義,形態學操作是一組根據影像形狀處理影像的操作。
在膨脹操作過程中,影像邊界會新增畫素,而在腐蝕操作過程中,影像邊界會移除多餘的畫素,在膨脹過程中新增的畫素總數取決於所用結構元素的尺寸。
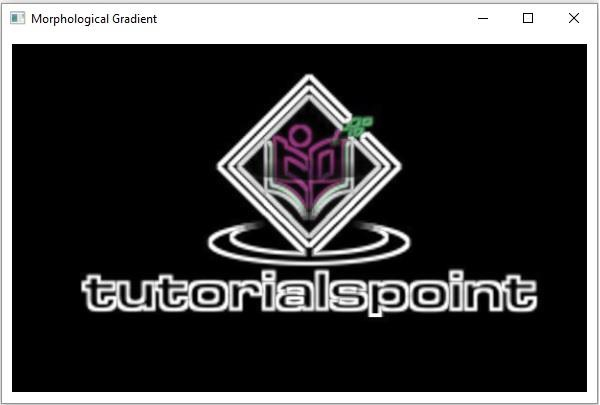
形態學梯度是一種操作,等於影像的膨脹和腐蝕之差。結果影像中的每個畫素值都表示鄰近畫素的對比度強度。這用於邊緣檢測、分割和查詢物件的輪廓。
示例
以下 Java 示例生成一個視窗,其中包含給定影像的形態學梯度 -
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.IOException;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.embed.swing.SwingFXUtils;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.image.ImageView;
import javafx.scene.image.WritableImage;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import org.opencv.core.Core;
import org.opencv.core.CvType;
import org.opencv.core.Mat;
import org.opencv.highgui.HighGui;
import org.opencv.imgcodecs.Imgcodecs;
import org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc;
public class MorphologicalGradient extends Application {
public void start(Stage stage) throws IOException {
//Loading the OpenCV core library
System.loadLibrary( Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME );
//Reading image data
String file ="D:\Images\morph_input1.jpg";
Mat src = Imgcodecs.imread(file);
//Creating destination matrix
Mat dst = new Mat(src.rows(), src.cols(), src.type());
//Preparing the kernel matrix object
Mat kernel = Mat.ones(5,5, CvType.CV_32F);
//Applying dilate on the Image
Imgproc.morphologyEx(src, dst, Imgproc.MORPH_GRADIENT, kernel);
//Converting matrix to JavaFX writable image
Image img = HighGui.toBufferedImage(dst);
WritableImage writableImage= SwingFXUtils.toFXImage((BufferedImage) img, null);
//Setting the image view
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(writableImage);
imageView.setX(10);
imageView.setY(10);
imageView.setFitWidth(575);
imageView.setPreserveRatio(true);
//Setting the Scene object
Group root = new Group(imageView);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 595, 400);
stage.setTitle("Morphological Gradient");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}輸入影像

輸出影像

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP