使用隨機樞軸的快速排序
快速排序是一種分治演算法。在這個演算法中,我們選擇一個樞軸元素,然後圍繞樞軸元素對陣列進行劃分。這兩個分割槽使得一部分包含所有小於樞軸元素的元素,另一部分包含所有大於樞軸元素的元素。類似地,每個部分都圍繞在每個部分中選擇的樞軸進一步劃分,這個過程一直執行到只剩下單個元素。
選擇樞軸
可以在陣列中選擇樞軸,方法如下:
隨機樞軸。
最右或最左元素作為樞軸。
中位數作為樞軸。
在本文中,我們將使用第一種方法來選擇樞軸並實現快速排序演算法。
問題陳述
給定一個數組。使用隨機樞軸的快速排序演算法對陣列進行排序。
示例1
Input: [3, 1, 7, 2, 10]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 7, 10]
說明 - 假設選擇3作為隨機樞軸,將其與10交換,然後將3設定為樞軸並使用3作為樞軸對陣列進行劃分。第一次劃分後,陣列為[1, 2, 3, 7, 10],其中3位於其排序位置。然後對3左側和右側的兩個子陣列呼叫函式,以對其餘陣列進行排序。
示例2
Input: [11, 32, 7, 90, 18, 34]
Output: [7, 11, 18, 32, 34, 90]
虛擬碼
Swap()函式的虛擬碼
procedure swap (*a, *b) temp = *a *a = *b *b = temp end procedure
pickRandom()函式的虛擬碼
procedure pickRandom (arr[], start, end) num = Random number between start and end swap arr[num] and arr[end] end procedure
partition()函式的虛擬碼
procedure partition (arr[], start, end)
pickRandom (arr, start, end)
pivot = arr[end]
i = start
for k = start to end - 1
if arr[k] <= pivot
swap arr[k] and arr[i]
i = i + 1
end if
end for
swap arr[i] and arr[end]
return i
end procedure
quickSort()函式的虛擬碼
procedure quickSort (arr[], start, end)
if start < end
p = pickRandom (arr[], start, end)
quickSort (arr[], start, p-1)
quickSort (arr[], p+1, end)
end if
end procedure
工作原理
讓我們取一個未排序的陣列,並從頭到尾呼叫staaquickSort()函式。
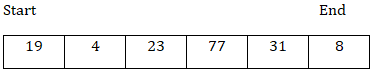
從pickRandom()函式開始,
假設num = start和end之間的隨機數 = 2
交換arr[1]和arr[end],我們得到以下陣列:
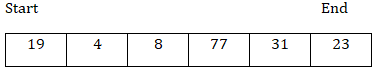
呼叫partition()函式後,
Pivot = arr[end] = 23
由於樞軸位於末尾,因此演算法從開頭開始向末尾移動。在迴圈中從start到end - 1取k,i = start
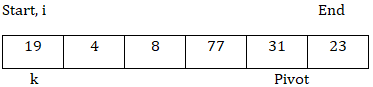
現在,arr[k] < arr[pivot],所以交換arr[k]和arr[i],i = i + 1。
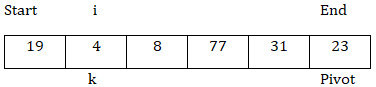
現在,arr[k] < arr[pivot],所以交換arr[k]和arr[i],i = i + 1。
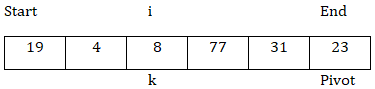
現在,arr[k] < arr[pivot],所以交換arr[k]和arr[i],i = i + 1。
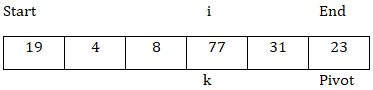
現在,arr[k] > arr[pivot],所以k向前移動。
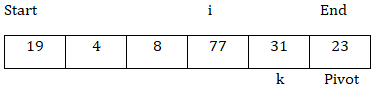
現在,arr[k] > arr[pivot]並且迴圈結束。
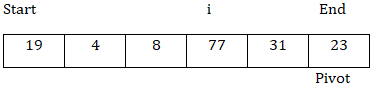
迴圈結束後,交換arr[i]和arr[pivot]。
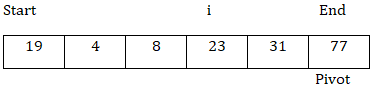
並返回i = 3。
因此,下一個quickSort()將對從start到i-1的陣列以及從i+1到end的陣列呼叫。
示例:C++實現
在下面的程式中,為了使用隨機樞軸對陣列進行快速排序,我們首先選擇陣列的隨機索引。然後將此隨機索引上的數字與陣列的末尾元素交換。然後選擇末尾元素作為樞軸。然後圍繞此樞軸對陣列進行劃分,並對劃分後的陣列遞迴呼叫quickSort,直到每個子陣列中只剩下一個元素。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to swap values of two variables
void swap(int *x, int *y){
int t = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = t;
}
// This function picks a random index between start and end and swaps the value at that index to the value at end index.
void pickRandom(int arr[], int start, int end){
int num = start + rand() % (end - start + 1);
swap(arr[num], arr[end]);
}
// This function calls the pickRandom() function and then partitions the array into two subarrays
int partition(int arr[], int start, int end){
pickRandom(arr, start, end);
// End element is chosen as pivot
int pivot = arr[end];
int i = start;
for (int k = start; k < end; k++){
if (arr[k] <= pivot){
swap(arr[k], arr[i]);
i++;
}
}
swap(arr[i], arr[end]);
// The array is divided into two sub-parts with the left part having all the elements smaller than the pivot and right part having elements bigger than the pivot.
return i;
}
void quickSort(int arr[], int start, int end){
if (start < end){
// p is the point of partition
int p = partition(arr, start, end);
// Calling quicksort on left subarray
quickSort(arr, start, p - 1);
// Calling quicksort on right subarray
quickSort(arr, p + 1, end);
}
}
int main(){
int arr[6] = {19, 4, 23, 77, 31, 8};
// Before Sorting
cout << "Array before sorting : ";
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Applying quick Sort
quickSort(arr, 0, 5);
// After Sorting
cout << "\nArray after sorting : ";
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Array before sorting : 19 4 23 77 31 8 Array after sorting : 4 8 19 23 31 77
時間複雜度 - 最壞情況複雜度 = O(n2)
平均(預期)情況複雜度 = O(nlogn)。
空間複雜度 - 由於使用了遞迴堆疊空間,因此為O(nlogn)。
結論
總之,使用帶有隨機樞軸的快速排序對陣列進行排序有助於將平均或預期時間複雜度提高到O(nlogn),但最壞情況複雜度仍然為O(n2)。


 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP