Python程式設計正規化
程式設計正規化是一種特定的程式設計方法或風格,它為設計和實現計算機程式提供了一個框架。它包含一組指導開發過程和程式碼結構的原則、概念和技術。不同的正規化有不同的解決問題、組織程式碼和表達計算的方法。
以下是Python中提供的各種程式設計正規化,它們使開發人員的工作更輕鬆、更高效。
程序式程式設計
程序式程式設計專注於將程式劃分成一系列過程或函式。在Python中,我們可以定義函式來執行特定任務,並使用過程式技術來構建我們的程式。
示例
在這個例子中,我們嘗試建立一個名為greet()的函式來執行問候給定名稱的特定任務。
def greet(name):
print("Hello, " + name + "!")
name = "Tutorialspoint"
greet(name)
輸出
Hello, Tutorialspoint!
面向物件程式設計 (OOPs)
OOPs是一種圍繞物件組織程式碼的正規化,物件是類的例項。Python完全支援OOPs,並提供諸如類、物件、繼承和多型性等功能。
示例
在這個例子中,我們建立不同的類,並在類中建立函式來實現特定任務。
class Animal:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def speak(self):
raise NotImplementedError("Subclass must implement this method.")
class Dog(Animal):
def speak(self):
return "Woof!"
class Cat(Animal):
def speak(self):
return "Meow!"
dog = Dog("Buddy")
print(dog.name)
print(dog.speak())
輸出
Buddy Woof!
指令式程式設計
指令式程式設計包括編寫指定計算機應遵循的詳細步驟的程式碼。Python作為一種通用語言,預設支援指令式程式設計。
示例
在這個例子中,我們嘗試建立一個程式來計算給定列表中所有元素的總和。
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
add = 0
for num in numbers:
add += num
print("Sum:", add)
輸出
Sum: 15
事件驅動程式設計
事件驅動程式設計通常用於圖形使用者介面 (GUI) 和網路程式設計。Python提供了像Tkinter和asyncio這樣的庫來支援事件驅動程式設計。
示例
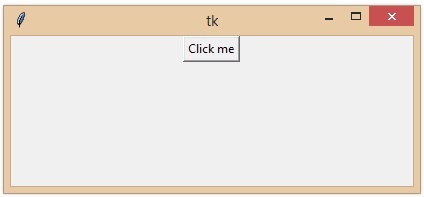
在這個例子中,我們使用tkinter庫建立一個GUI按鈕。
from tkinter import Tk, Button
def button_click():
print("Button clicked!")
root = Tk()
button = Button(root, text="Click me", command=button_click)
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
print("Button created")
輸出
Button created
函數語言程式設計
函數語言程式設計強調不變性和純函式的使用。Python支援函數語言程式設計的概念,例如高階函式、lambda函式和列表推導式。
示例
在這個例子中,我們使用map、lambda和filter建立了一個函式式程式,用於查詢列表中給定數字的平方,並列印給定列表中的偶數。
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squares = list(map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers))
print("The square of the numbers in the list",squares)
even_numbers = list(filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers))
print("The even numbers from the given list",even_numbers)
輸出
The square of the numbers in the list [1, 4, 9, 16, 25] The even numbers from the given list [2, 4]

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP