使用 Python 將兩個多項式(以連結串列形式給出)相加的程式
假設我們有兩個多項式,我們需要求這兩個多項式的和。多項式需要用連結串列表示;多項式的項將用連結串列節點表示。每個連結串列節點將包含係數值、冪值以及指向下一個連結串列節點的指標。我們需要返回第三個連結串列,它是兩個連結串列多項式的和。
所以,如果輸入類似於
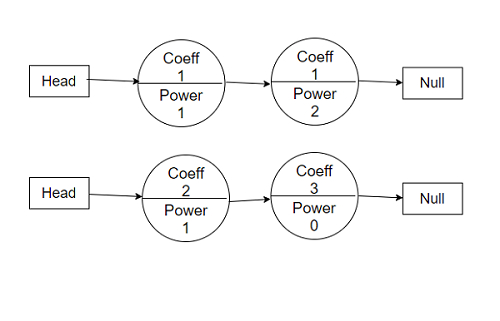
1x^1 + 1x^2 = 0 和 2x^1 + 3x^0 = 0,
那麼輸出將是 3x^1 + 1x^2 + 3x^0 = 0
為了解決這個問題,我們將遵循以下步驟 -
dummy := 一個新的多項式節點
node := 一個新的多項式節點
當 poly1 和 poly2 不為空時,執行以下操作
如果 poly1 的冪 > poly2 的冪,則
node 的下一個 := poly1
node := poly1
poly1 := poly1 的下一個
否則,當 poly1 的冪 < poly2 的冪時,則
node 的下一個 := poly2
node := poly2
poly2 := poly2 的下一個
否則,
coef := poly1 的係數 + poly2 的係數
如果 coef 不為零,則
poly1 := poly1 的下一個
poly2 := poly2 的下一個
node 的下一個 := poly1 或 poly2
返回 dummy 的下一個
讓我們看看下面的實現,以便更好地理解 -
示例
class polynomial: def __init__(self, coeff = 0, pow = 0, nxt = None): self.coefficient = coeff self.power = pow self.next = nxt def create_poly(expression): head = None for element in expression: if head == None: head = polynomial(element[0], element[1]) else: temp = head while temp.next != None: temp = temp.next if temp.next == None: temp.next = polynomial(element[0], element[1]) return head def show_poly(head): temp = head while temp.next != None: print(str(temp.coefficient) + 'x^' + str(temp.power), end = ' + ') temp = temp.next if temp.next == None: print(str(temp.coefficient) + 'x^' + str(temp.power), end=' = 0') def solve(poly1, poly2): dummy = node = polynomial() while poly1 and poly2: if poly1.power > poly2.power: node.next = node = poly1 poly1 = poly1.next elif poly1.power < poly2.power: node.next = node = poly2 poly2 = poly2.next else: coef = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient if coef: node.next = node = polynomial(coef, poly1.power) poly1 = poly1.next poly2 = poly2.next node.next = poly1 or poly2 return dummy.next poly1 = create_poly([[1,1], [1,2]]) poly2 = create_poly([[2,1], [3, 0]]) poly3 = solve(poly1, poly2) show_poly(poly3)
輸入
poly1 = create_poly([[1,1], [1,2]]) poly2 = create_poly([[2,1], [3, 0]])
輸出
3x^1 + 1x^2 + 3x^0 = 0

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係型資料庫管理系統
關係型資料庫管理系統 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP