Linux 系統中的程序表示
Linux 可以管理系統中的程序,每個程序都由一個 task_struct C 資料結構表示。它位於核心原始碼目錄中的 <linux/sched.h> include 檔案中。任務向量是一個指向系統中每個 task_struct 資料結構的指標陣列。除了普通型別的程序之外,Linux 還支援即時程序。所有所需的資訊,即程序狀態、排程和記憶體管理資訊、開啟檔案列表以及指向程序父級和子程序及兄弟程序列表的指標都包含在此結構中。
建立程序的程序稱為該建立程序的父程序;其子程序是其建立的任何程序,兄弟程序是具有相同父程序的子程序。
其中一些欄位包含 −
long state; /*denote state of the process */ struct sched entity se; /*denote scheduling information */ struct task struct *parent; /*denotes this process’s parent */ struct list head children; /*denotes this process’s children */ struct files struct *files; /* denotes list of open files */ struct mm struct *mm; /* denotes address space of this process */ struct task struct *p_opptr,*p_pptr,*p_cptr,*p_ysptr,*p_osptr /*denotes, op = original parent, p = parent, c = youngest child, ys = youngest sibling, os = older sibling */
Linux 核心中,所有活動程序都使用 task struct 的雙向連結串列表示。核心對當前在系統上執行的程序維持一個指標 -current-,如下所示 −
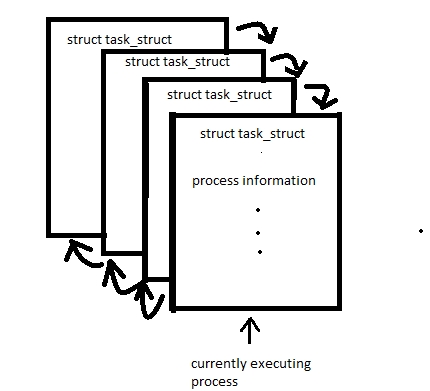
例如,如果系統希望將當前正在執行的程序狀態更改為新狀態。如果 current 是指向當前正在執行的程序的指標,則使用以下方式更改其狀態:current->state = new state;

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP