C++ 中兩個連結串列的交集
連結串列是一種線性資料結構,其中每個節點有兩個塊,一個塊包含節點的值或資料,另一個塊包含下一個欄位的地址。
假設我們有一個連結串列,每個節點都包含一個隨機指標,該指標指向列表中的其他節點。任務是找到兩個連結串列相互交叉的節點。如果它們沒有交集,則返回 NULL 或空作為輸出。
例如
輸入-1
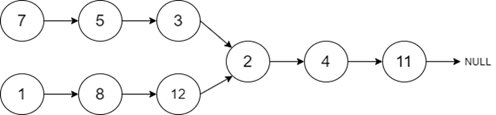
輸出
2
說明:由於給定的連結串列在值為“2”的節點處相交,因此我們將返回“2”作為輸出。
輸入-2
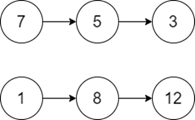
輸出
NULL
說明:由於沒有公共點,因此在這種情況下我們將返回 NULL。
解決此問題的方法
我們有兩個連結串列,它們在某個公共點相互交叉。為了找到交點,我們將遍歷這兩個連結串列,直到我們發現它們都指向相同的值。在某些時候,連結串列的下一個節點的指標將相同。因此,我們將返回該點的值。
- 取兩個連結串列,分別包含資料和指向下一個節點的指標。
- 一個函式 commonPoint(listnode*headA, listnode*headB) 分別接收兩個連結串列的指標,並返回連結串列的公共點或交點的值。
- 一個查詢連結串列長度的整數函式將返回從列表頭部開始的兩個連結串列的長度。
- 現在建立一個指向兩個列表頭的指標,並遍歷長度較長的列表,直到 (第一個列表的長度 - 第二個列表的長度)。
- 現在遍歷列表,直到我們找到下一個指標相等。
- 返回這兩個列表相交的特定節點的值。
示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class listnode {
public:
int data;
listnode * next;
};
// Find the length of the linked list
int count(listnode * head) {
int count = 0;
while (head != NULL) {
count++;
head = head -> next;
}
return count;
}
//Function to get the common point of two linked list
int commonPoint(listnode * headA, listnode * headB) {
int len1 = count(headA);
int len2 = count(headB);
listnode * p1 = headA;
listnode * p2 = headB;
if (len1 > len2) {
for (int i = 0; i < len1 - len2; ++i) {
p1 = p1 -> next;
}
}
if (len1 < len2) {
for (int i = 0; i < len2 - len1; ++i) {
p2 = p2 -> next;
}
}
while (p1 != NULL and p2 != NULL) {
if (p1 == p2) {
return p1 -> data;
}
p1 = p1 -> next;
p2 = p2 -> next;
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
listnode * head;
listnode * headA = new listnode();
headA -> data = 5;
listnode * headB = new listnode();
headB -> data = 4;
head = new listnode();
head -> data = 9;
headB -> next = head;
head = new listnode();
head -> data = 2;
headB -> next -> next = head;
head = new listnode();
head -> data = 7;
headA -> next = head;
headB -> next -> next -> next = head;
head = new listnode();
head -> data = 3;
headA -> next -> next = head;
headA -> next -> next -> next = NULL;
cout << commonPoint(headA, headB) << endl;
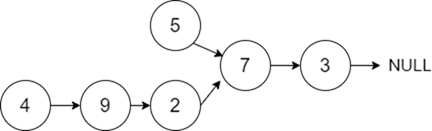
}執行以上程式碼將生成以下輸出:
輸出
7
說明:給定的連結串列在“7”處合併。

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 RDBMS
RDBMS 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP