如何在Android中從IntentService共享Intent?
在進入示例之前,我們應該瞭解Android中的Intent Service是什麼。Intent Service將非同步執行後臺操作。當用戶從活動中呼叫startService()時,它不會為每個請求建立例項。它將在服務類中完成某些操作後停止服務,否則我們需要使用stopSelf()停止服務。
此示例演示如何從IntentService共享Intent。
步驟1 - 在Android Studio中建立一個新專案,轉到檔案 ⇒ 新建專案,並填寫所有必需的詳細資訊以建立一個新專案。
步驟2 - 將以下程式碼新增到res/layout/activity_main.xml。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools = "http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "match_parent"
tools:context = ".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id = "@+id/text"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Start Service"
android:textSize = "25sp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf = "parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf = "parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf = "parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf = "parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>在上面的程式碼中,我們使用了TextView。當用戶點選TextView時,它將開啟Android作業系統的預設共享對話方塊。
步驟3 - 將以下程式碼新增到src/MainActivity.java
package com.example.andy.myapplication;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
text = findViewById(R.id.text);
text.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
startService(new Intent(MainActivity.this, service.class));
}
});
}
}建立一個名為service.class的檔案並新增以下程式碼 –
package com.example.andy.myapplication;
import android.app.IntentService;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class service extends IntentService {
public static volatile boolean shouldStop = false;
public service() {
super(service.class.getSimpleName());
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
Intent sharingIntent = new Intent(android.content.Intent.ACTION_SEND);
sharingIntent.setType("text/plain");
sharingIntent.putExtra(android.content.Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, "Subject Here");
sharingIntent.putExtra(android.content.Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, "Tutorialspoint.com");
startActivity(Intent.createChooser(sharingIntent, "Sharing"));
if(shouldStop) {
stopSelf();
return;
}
}
}要在服務類中停止服務,請使用以下程式碼 –
stopSelf();
步驟4 - 將以下程式碼新增到manifest.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package = "com.example.andy.myapplication"> <uses-permission android:name = "android.permission.WAKE_LOCK"/> <application android:allowBackup = "true" android:icon = "@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label = "@string/app_name" android:roundIcon = "@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl = "true" android:theme = "@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name = ".MainActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name = "android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name = "android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <service android:name = ".service"/> </application> </manifest>
讓我們嘗試執行您的應用程式。我假設您已將您的實際Android移動裝置連線到您的計算機。要從Android Studio執行應用程式,請開啟您的一個專案活動檔案,然後單擊執行 ![]() 工具欄中的圖示。選擇您的移動裝置作為選項,然後檢查您的移動裝置,它將顯示您的預設螢幕 –
工具欄中的圖示。選擇您的移動裝置作為選項,然後檢查您的移動裝置,它將顯示您的預設螢幕 –
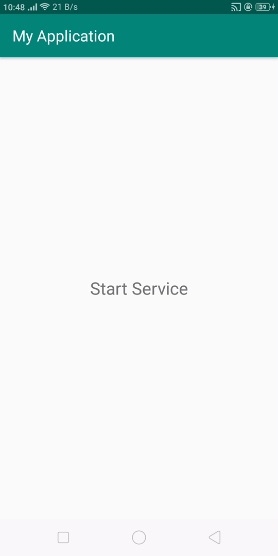
在上面的結果中,它顯示了應用程式的預設螢幕。當用戶點選TextView時,它將顯示來自移動作業系統的預設共享對話方塊,如下所示 –

點選 這裡 下載專案程式碼

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統(RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP