C++ 中的多級連結串列扁平化
在這個問題中,我們給定一個多級連結串列。我們的任務是建立一個程式來扁平化這個多級連結串列。
扁平化操作以這樣的方式進行:第一級節點將首先出現在連結串列中,然後是第二級節點。
**多級連結串列**是一種多維資料結構,其中連結串列的每個節點都有兩個連結指標,一個指向下一個節點的連結,另一個指向具有一個或多個節點的子列表。此子指標可能指向或可能不指向其他列表節點。
示例
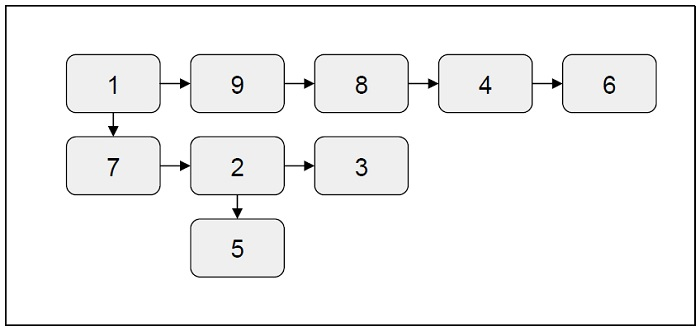
讓我們來看一個例子來理解這個問題
輸入

輸出
1-> 9-> 8 -> 4 -> 6-> 7-> 2-> 3-> 5
解決方案方法
解決這個問題的一個簡單方法是使用類似於層序遍歷的演算法。我們將從第一個節點開始遍歷連結串列,並遍歷同一層的所有節點。如果節點存在任何子指標,則使用尾指標將其移動到當前連結串列的末尾。然後遞迴地對連結串列的每個子節點執行相同的遍歷。下面的程式將更好地闡述該邏輯。
示例
演示我們解決方案工作的程式
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define SIZE(arr) (sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]))
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node *child;
};
Node *createList(int *arr, int n){
Node *head = NULL;
Node *p;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i){
if (head == NULL)
head = p = new Node();
else{
p->next = new Node();
p = p->next;
}
p->data = arr[i];
p->next = p->child = NULL;
}
return head;
}
Node *createList(void){
int arr1[] = {1, 9, 8, 4, 6};
int arr2[] = {7, 3, 2};
int arr3[] = {5};
Node *head1 = createList(arr1, (sizeof(arr1)/sizeof(arr1[0])));
Node *head2 = createList(arr2, (sizeof(arr2)/sizeof(arr2[0])));
Node *head3 = createList(arr3, (sizeof(arr3)/sizeof(arr3[0])));
head1->child = head2;
head1->next->child = head3;
return head1;
}
void flattenLinkedList(Node *head){
if (head == NULL)
return;
Node *tmp;
Node *tail = head;
while (tail->next != NULL)
tail = tail->next;
Node *cur = head;
while (cur != tail){
if (cur->child){
tail->next = cur->child;
tmp = cur->child;
while (tmp->next)
tmp = tmp->next;
tail = tmp;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
int main(void){
Node *head = NULL;
head = createList();
flattenLinkedList(head);
cout<<"The flattened Linked List is ";
while (head != NULL){
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}輸出
The flattened Linked List is 1 9 8 4 6 7 3 2 5

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP