作業系統中無死鎖條件的C++程式
給定記憶體中P個程序和它們完成執行所需的N個資源,任務是找到應該分配給程序的最小資源數R,以確保永遠不會發生死鎖。
什麼是死鎖
死鎖是作業系統中的一種情況,其中多個駐留在記憶體中的程序無法執行,因為程式執行所需的資源被另一個正在等待其他資源完成的資源持有。
假設記憶體中有兩個程序P1和P2,P1需要資源R1,P2需要資源R2,但是當P1持有資源R2並等待資源R1,而P2持有資源R1並等待資源R2時,就會發生死鎖。
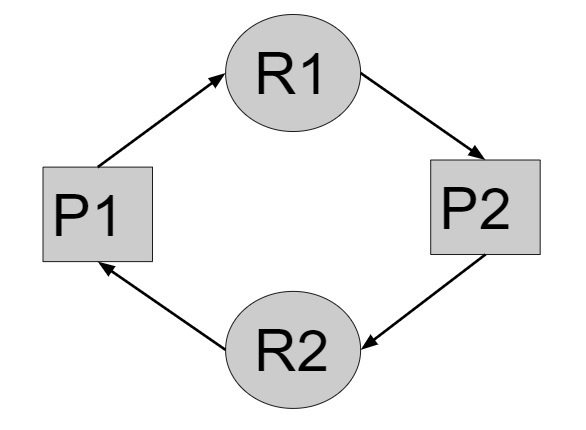
這是一個迴圈等待的例子,這是死鎖的原因之一。因此,為了防止死鎖,我們需要計算應該為程序提供的資源數量,以確保不會發生死鎖。
無死鎖條件
R >= P * (N - 1) + 1
其中,R是資源數,P是程序數,N是程序的需求數
示例
Input-: processes = 5, need = 3 Output-: minimum required resources are: 11 Input-: Processes = 7, need = 2 Output-: minimum required resources are: 8
下面程式中使用的演算法如下:
- 輸入記憶體中程序的數量和程序的需求。
- 應用給定的公式計算所需的資源數量。
- 顯示結果。
演算法
START Step 1-> declare function to calculate the minimum number of resources needed int min_resource(int process, int need) declare int calculate = 0 set calculate = process * (need - 1) + 1 return calculate Step 2-> In main() Declare int process = 5 and need = 3 Call min_resource(process, need) STOP
示例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//calculate minimum number of resources needed
int min_resource(int process, int need) {
int calculate = 0;
calculate = process * (need - 1) + 1;
return calculate;
}
int main() {
int process = 5, need = 3;
cout << "minimum required resources are : " <<min_resource(process, need);
return 0;
}輸出
minimum required resources are : 11

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C程式設計
C程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP