將SD卡連線到Arduino並獲取卡資訊
在本教程中,我們將Arduino Uno連線到SD卡並提取卡資訊。
電路圖
電路圖如下所示:
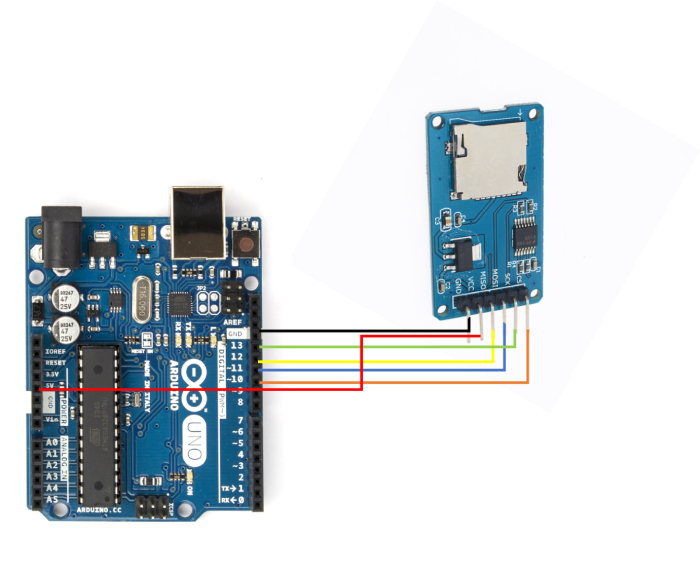
如您所見,您需要進行以下連線:
| SD卡座 | Arduino Uno |
|---|---|
| Vcc | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| MISO | 12 |
| MOSI | 11 |
| SCK | 13 |
| CS | 10 |
只有對於Vcc,請確保您的SD卡座輸入電壓為5V。如果輸入電壓為3.3V,請將其連線到Arduino Uno上的3.3V引腳。
程式碼詳解
我們將逐步講解內建SD庫附帶的示例程式碼。您可以從檔案→示例→SD→CardInfo中訪問它。

或者,您也可以在GitHub上訪問它:https://github.com/arduinolibraries/SD/blob/master/examples/CardInfo/CardInfo.ino
我們首先包含SPI和SD庫:
#include <SPI.h> #include <SD.h>
接下來,我們根據SD庫中定義的物件定義一些變數。
Sd2Card card; SdVolume volume; SdFile root;
接下來,我們定義晶片選擇引腳。示例程式碼將晶片選擇設定為4號引腳。但是,我們將CS引腳連線到Arduino Uno的10號引腳。因此,我們將更改它。
const int chipSelect = 10;
在Setup中,我們首先初始化Serial,然後初始化SD卡(使用晶片選擇引腳和SPI協議,SPI協議的其他引腳MISO、MOSI、SCK在SPI庫中預設定義)。
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
Serial.print("
Initializing SD card...");
// we'll use the initialization code from the utility libraries
// since we're just testing if the card is working!
if (!card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED, chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed. Things to check:");
Serial.println("* is a card inserted?");
Serial.println("* is your wiring correct?");
Serial.println("* did you change the chipSelect pin to match your
shield or module?");
while (1);
} else {
Serial.println("Wiring is correct and a card is present.");
}接下來,我們使用.type()函式獲取並列印卡的型別。
// print the type of card
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Card type: ");
switch (card.type()) {
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1:
Serial.println("SD1");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2:
Serial.println("SD2");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC:
Serial.println("SDHC");
break;
default:
Serial.println("Unknown");
}接下來,我們初始化卡的卷,獲取卡中的簇總數和每個簇的塊數,從而獲得卡中的塊總數。
// Now we will try to open the 'volume'/'partition' - it should be
FAT16 or FAT32
if (!volume.init(card)) {
Serial.println("Could not find FAT16/FAT32 partition.
Make sure you've formatted the card");
while (1);
}
Serial.print("Clusters: ");
Serial.println(volume.clusterCount());
Serial.print("Blocks x Cluster: ");
Serial.println(volume.blocksPerCluster());
Serial.print("Total Blocks: ");
Serial.println(volume.blocksPerCluster() * volume.clusterCount());
Serial.println();之後,我們列印卷是FAT 16還是FAT 32型別。此外,我們還計算總容量(以kB為單位),利用一個塊始終為512位元組或0.5 kB這一事實。
// print the type and size of the first FAT-type volume
uint32_t volumesize;
Serial.print("Volume type is: FAT");
Serial.println(volume.fatType(), DEC);
volumesize = volume.blocksPerCluster(); // clusters are collections of blocks
volumesize *= volume.clusterCount(); // we'll have a lot of clusters
volumesize /= 2; // SD card blocks are always 512 bytes (2 blocks are 1KB)
Serial.print("Volume size (Kb): ");
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Mb): ");
volumesize /= 1024;
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Gb): ");
Serial.println((float)volumesize / 1024.0);最後,我們使用openRoot()函式列出卡上找到的所有檔案,並列印日期、大小以及檔名。
Serial.println("
Files found on the card (name, date and size in bytes): ");
root.openRoot(volume);
// list all files in the card with date and size
root.ls(LS_R | LS_DATE | LS_SIZE);

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP