使用雙向連結串列在任意位置插入節點的C程式
連結串列使用動態記憶體分配,是節點的集合。
節點有兩個部分:資料和連結。
連結串列型別
C 程式語言中的連結串列型別如下:
- 單向連結串列。
- 雙向連結串列。
- 迴圈單向連結串列。
- 迴圈雙向連結串列。
雙向連結串列
下圖顯示了雙向連結串列的表示。
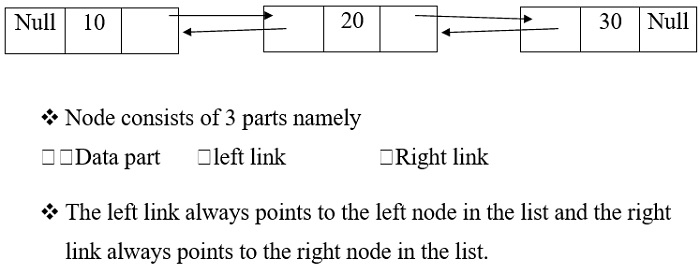
示例
以下是使用雙向連結串列**在任意位置插入節點的 C 程式**:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int num;
struct node * preptr;
struct node * nextptr;
}*stnode, *ennode;
void DlListcreation(int n);
void DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning(int num);
void DlLinsertNodeAtEnd(int num);
void DlLinsertNodeAtAny(int num, int pos);
void displayDlList(int a);
int main(){
int n,num1,a,insPlc;
stnode = NULL;
ennode = NULL;
printf("
Doubly Linked List : Insert a node at any position :
");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
");
printf(" Input the number of nodes : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
DlListcreation(n);
a=1;
displayDlList(a);
printf(" Input the position ( 1 to %d ) to insert a new node : ",n+1);
scanf("%d", &insPlc);
printf(" Input data for the position %d : ", insPlc);
scanf("%d", &num1);
DlLinsertNodeAtAny(num1,insPlc);
a=2;
displayDlList(a);
return 0;
}
void DlListcreation(int n){
int i, num;
struct node *fnNode;
if(n >= 1){
stnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(stnode != NULL){
printf(" Input data for node 1 : "); // assigning data in the first node
scanf("%d", &num);
stnode->num = num;
stnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode = stnode;
for(i=2; i<=n; i++){
fnNode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(fnNode != NULL){
printf(" Input data for node %d : ", i);
scanf("%d", &num);
fnNode->num = num;
fnNode->preptr = ennode;
fnNode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode->nextptr = fnNode;
ennode = fnNode;
}
else{
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
break;
}
}
}
else{
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
}
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtAny(int num, int pos){
int i;
struct node * newnode, *tmp;
if(ennode == NULL){
printf(" No data found in the list!
");
}
else{
tmp = stnode;
i=1;
while(i<pos-1 && tmp!=NULL){
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
i++;
}
if(pos == 1){
DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning(num);
}
else if(tmp == ennode){
DlLinsertNodeAtEnd(num);
}
else if(tmp!=NULL){
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = tmp->nextptr;
newnode->preptr = tmp;
if(tmp->nextptr != NULL){
tmp->nextptr->preptr = newnode; // n+1th node is linking with new node
}
tmp->nextptr = newnode; // n-1th node is linking with new node
}
else{
printf(" The position you entered, is invalid.
");
}
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning(int num){
struct node * newnode;
if(stnode == NULL){
printf(" No data found in the list!
");
}
else{
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = stnode;
newnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->preptr = newnode;
stnode = newnode;
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtEnd(int num){
struct node * newnode;
if(ennode == NULL){
printf(" No data found in the list!
");
}
else{
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = NULL;
newnode->preptr = ennode;
ennode->nextptr = newnode;
ennode = newnode;
}
}
void displayDlList(int m){
struct node * tmp;
int n = 1;
if(stnode == NULL) {
printf(" No data found in the List yet.");
}
else{
tmp = stnode;
if (m==1) {
printf("
Data entered in the list are :
");
}
else{
printf("
After insertion the new list are :
");
}
while(tmp != NULL){
printf(" node %d : %d
", n, tmp->num);
n++;
tmp = tmp->nextptr; // current pointer moves to the next node
}
}
}輸出
執行上述程式後,會產生以下結果:
Doubly Linked List : Insert node at any position: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Input the number of nodes : 5 Input data for node 1 : 23 Input data for node 2 : 12 Input data for node 3 : 11 Input data for node 4 : 34 Input data for node 5 : 10 Data entered in the list are : node 1 : 23 node 2 : 12 node 3 : 11 node 4 : 34 node 5 : 10 Input the position ( 1 to 6 ) to insert a new node : 5 Input data for the position 5 : 78 After insertion the new list are : node 1 : 23 node 2 : 12 node 3 : 11 node 4 : 34 node 5 : 78 node 6 : 10

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP