JavaScript 中的雙向連結串列
在本文中,我們將討論 JavaScript 中的雙向連結串列類資料結構。 這是一種線性資料結構。 雙向連結串列在所有操作中幾乎與單向連結串列相同,我們只需要每節點額外跟蹤一個連結。 在單向連結串列中,我們只有下一個連結,在雙向連結串列中,我們有 2 個連結,下一個和上一個。
雙向連結串列表示為 −
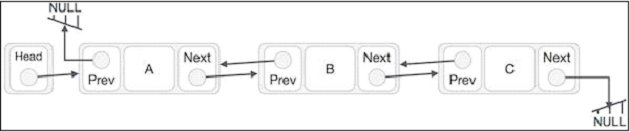
請注意,在類本身中,我們還需要跟蹤尾部(最後一個元素)。
示例
在此示例中,我們瞭解雙向連結串列及其在 JavaScript 中的操作。 在這裡,我們在向其中插入資料時建立列表; 在從中刪除資料時可能刪除節點。 我們還使用使用者定義的方法列印() 列印列表。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Doubly Linked List Data Structure</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function createNode(value) {
return {
value: value,
next: null,
previous: null,
};
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
insert(value) {
this.size++;
let newNode = createNode(value);
if (this.tail) {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.previous = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
return newNode;
}
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
return newNode;
}
remove() {
if (this.tail) {
this.size--;
let removedTail = this.tail;
let beforeTail = this.tail.previous;
this.tail = beforeTail;
if (this.tail) {
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
this.head = null;
}
return removedTail;
}
return undefined;
}
print() {
document.write("The Elements in the Doubly Linked List are :</br> ");
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
document.write(
`${current.previous?.value} ${current.value} ${current.next?.value}`
);
current = current.next;
}
}
insertHead(value) {
this.size++;
let newNode = createNode(value);
if (this.head) {
this.head.previous = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
return newNode;
}
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
return newNode;
}
insertIndex(value, index) {
if (index >= this.size) {
throw new Error("Insert index out of bounds");
}
if (index === 0) {
return this.insertHead(value);
}
this.size++;
let currentNode = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
let previousNode = currentNode.previous;
let newNode = createNode(value);
newNode.next = currentNode;
newNode.previous = previousNode;
previousNode.next = newNode;
currentNode.previous = newNode;
return newNode;
}
}
let dLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList();
dLinkedList.insert(7);
dLinkedList.insert(8);
dLinkedList.insert(9);
dLinkedList.print();
</script>
</body>
</html>

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路技術
網路技術 關係型資料庫
關係型資料庫 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C 程式設計
C 程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP